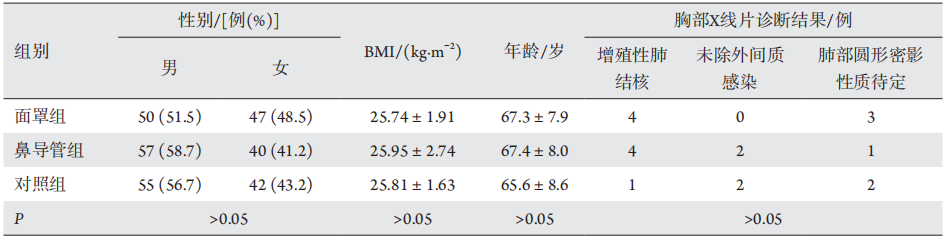
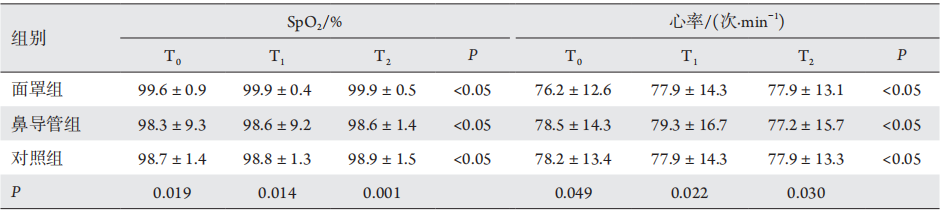
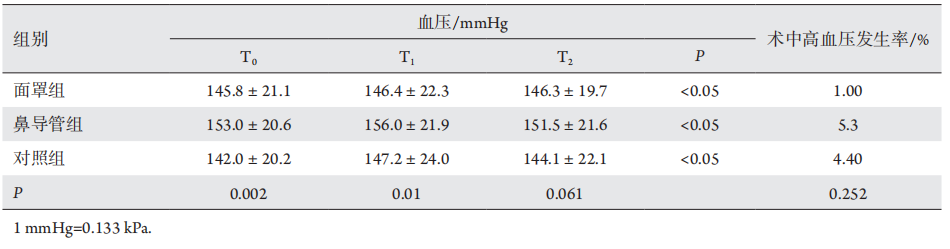
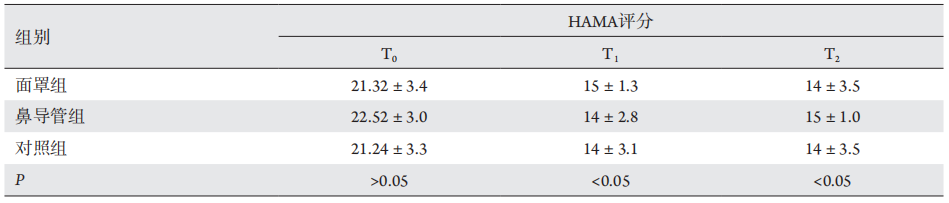
1、Church ML, Priehs DR, Denis H, et al. Technique, postoperativecomplications, and visual outcomes of phacoemulsification cataract surgery in 21 penguins (27 eyes): 2011—2015[ J]. Vet Ophthalmol, 2018, 21(6): 612-621.Church ML, Priehs DR, Denis H, et al. Technique, postoperativecomplications, and visual outcomes of phacoemulsification cataract surgery in 21 penguins (27 eyes): 2011—2015[ J]. Vet Ophthalmol, 2018, 21(6): 612-621.
2、裴双平. 超声乳化治疗白内障合并症的临床价值研究[ J]. 当代医学, 2015, 21(3): 52-53.
PEI Shuangping. Clinical value of Phacoemulsification in the treatment of cataract[ J]. Contemporary Medicine, 2015, 21(3): 52-53.裴双平. 超声乳化治疗白内障合并症的临床价值研究[ J]. 当代医学, 2015, 21(3): 52-53.
PEI Shuangping. Clinical value of Phacoemulsification in the treatment of cataract[ J]. Contemporary Medicine, 2015, 21(3): 52-53.
3、郝艳洁, 吴雨玻, 李明, 等. 白色白内障超声乳化治疗效果[ J]. 齐鲁医学杂志, 2016, 31(1): 67-68.
HAO Yanjie, WU Yubo, LI Ming, et al. Effect of phacoemulsification on white cataract[ J]. Medical Journal of Qilu, 2016, 31(1): 67-68.郝艳洁, 吴雨玻, 李明, 等. 白色白内障超声乳化治疗效果[ J]. 齐鲁医学杂志, 2016, 31(1): 67-68.
HAO Yanjie, WU Yubo, LI Ming, et al. Effect of phacoemulsification on white cataract[ J]. Medical Journal of Qilu, 2016, 31(1): 67-68.
4、李卫红. 白内障超声乳化手术的手术室护理效果研究[ J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2018, 18(37): 240, 242.
LI Weihong. Study on nursing effect of cataract phacoemulsification in operating room[ J]. World Latest Medicine, 2018, 18(37): 240, 242.李卫红. 白内障超声乳化手术的手术室护理效果研究[ J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘, 2018, 18(37): 240, 242.
LI Weihong. Study on nursing effect of cataract phacoemulsification in operating room[ J]. World Latest Medicine, 2018, 18(37): 240, 242.
5、Cummings AB, K?nig HL. Effect of oxygen and air inhalation during cataract surgery on blood gas parameters[ J]. J Cataract Refract Surg, 1996, 22(9): 1236-1239.Cummings AB, K?nig HL. Effect of oxygen and air inhalation during cataract surgery on blood gas parameters[ J]. J Cataract Refract Surg, 1996, 22(9): 1236-1239.
6、Risdall JE, Geraghty IF. Oxygenation of patients undergoing ophthalmic surgery under local anaesthesia[ J]. Anaesthesia, 1997, 52(5): 492-495.Risdall JE, Geraghty IF. Oxygenation of patients undergoing ophthalmic surgery under local anaesthesia[ J]. Anaesthesia, 1997, 52(5): 492-495.
7、Iamsukhon M, Kulpapangkorn P, Hirunwiwatkul P, et al. Effectiveness of oxygenation under the drape in phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation: a randomized clinical trial[ J]. J Med Assoc Thai, 2006, 89(3): 343-349.Iamsukhon M, Kulpapangkorn P, Hirunwiwatkul P, et al. Effectiveness of oxygenation under the drape in phacoemulsification with intraocular lens implantation: a randomized clinical trial[ J]. J Med Assoc Thai, 2006, 89(3): 343-349.
8、Khezri MB, Oladi MR, Atlasbaf A. Effect of melatonin and gabapentin on anxiety and pain associated with retrobulbar eye block for cataract surgery: A randomized double-blind study[ J]. Indian J Pharmacol, 2013, 45(6): 581-586.Khezri MB, Oladi MR, Atlasbaf A. Effect of melatonin and gabapentin on anxiety and pain associated with retrobulbar eye block for cataract surgery: A randomized double-blind study[ J]. Indian J Pharmacol, 2013, 45(6): 581-586.
9、潘承云. 蛛网膜下腔出血患者焦虑心理护理干预的效果观察[ J]. 当代护士(上旬刊), 2016(5): 132-133.
PAN Chengyun. effect of psychological nursing intervention on anxiety of subarachnoid hemorrhage patients[ J]. Today Nurse, 2016(5): 132-133.潘承云. 蛛网膜下腔出血患者焦虑心理护理干预的效果观察[ J]. 当代护士(上旬刊), 2016(5): 132-133.
PAN Chengyun. effect of psychological nursing intervention on anxiety of subarachnoid hemorrhage patients[ J]. Today Nurse, 2016(5): 132-133.
10、王肖萍, 吕秀平. 激励式护理模式在永久性结肠造口术围术期护理中的应用[ J]. 护理研究, 2018, 32(23): 3805-3806.
WANG Xiaoping, Lü Xiuping. application of incentive nursing model in perioperative nursing of patients undergoing permanent
colostomy[ J]. Chinese Nursing Research, 2018, 32(23): 3805-3806.王肖萍, 吕秀平. 激励式护理模式在永久性结肠造口术围术期护理中的应用[ J]. 护理研究, 2018, 32(23): 3805-3806.
WANG Xiaoping, Lü Xiuping. application of incentive nursing model in perioperative nursing of patients undergoing permanent
colostomy[ J]. Chinese Nursing Research, 2018, 32(23): 3805-3806.
11、曹克妮. 程序化护理对白内障超声乳化术患者术后视力恢复的影响[ J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2016, 25(21): 2386-2388.
CAO Keni. effect of programmed nursing on postoperative visual acuity of patients undergoing phacoemulsification[ J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2016, 25(21): 2386-2388.曹克妮. 程序化护理对白内障超声乳化术患者术后视力恢复的影响[ J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2016, 25(21): 2386-2388.
CAO Keni. effect of programmed nursing on postoperative visual acuity of patients undergoing phacoemulsification[ J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2016, 25(21): 2386-2388.
12、斯妍娜, 施韬, 鲍红光. 全麻诱导中右旋美托咪定的镇静效应及对丙泊酚用量的影响[ J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2010, 26(12):1053-1055.
SI Yanna , SHI Tao, BAO Hongguang . the influence of dexmedetomidine on sedation and requirement of propofol during
anesthesia induction[ J]. The Journal of Clinical Anesthesiology, 2010, 26(12): 1053-1055.斯妍娜, 施韬, 鲍红光. 全麻诱导中右旋美托咪定的镇静效应及对丙泊酚用量的影响[ J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2010, 26(12):1053-1055.
SI Yanna , SHI Tao, BAO Hongguang . the influence of dexmedetomidine on sedation and requirement of propofol during
anesthesia induction[ J]. The Journal of Clinical Anesthesiology, 2010, 26(12): 1053-1055.
13、罗金花. 全麻时应用可视喉镜行保留自主呼吸气管插管的护理配合[ J]. 南通大学学报(医学版), 2014, 34(6): 549-550.
LUO Jinhua. Nursing Cooperation of self-breathing tracheal intubation with visual laryngoscope during general anesthesia[ J]. Journal of Nantong University. Medical Sciences, 2014, 34(6): 549-550.罗金花. 全麻时应用可视喉镜行保留自主呼吸气管插管的护理配合[ J]. 南通大学学报(医学版), 2014, 34(6): 549-550.
LUO Jinhua. Nursing Cooperation of self-breathing tracheal intubation with visual laryngoscope during general anesthesia[ J]. Journal of Nantong University. Medical Sciences, 2014, 34(6): 549-550.
14、包崇玲, 俞英, 叶爱素. 蓝牙耳机唤醒功能在老年患者眼科手术中的应用[ J]. 中国乡村医药, 2020, 27(11): 74-75.
BAO Chongling, YU Ying, YE Aisu. Application of Bluetooth headset wake-up function in senile patients undergoing ophthalmic surgery[ J]. Chinese Journal of Rural Medicine and Pharmacy, 2020, 27(11): 74-75.包崇玲, 俞英, 叶爱素. 蓝牙耳机唤醒功能在老年患者眼科手术中的应用[ J]. 中国乡村医药, 2020, 27(11): 74-75.
BAO Chongling, YU Ying, YE Aisu. Application of Bluetooth headset wake-up function in senile patients undergoing ophthalmic surgery[ J]. Chinese Journal of Rural Medicine and Pharmacy, 2020, 27(11): 74-75.
15、张津方, 周畅. 情绪安抚护理运用在眼外伤致眼球摘除术患者中的护理效果分析[ J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2017, 28(S3):642-643.
ZHANG Jinfang, ZHOU Chang. analysis of the effect of emotional comfort nursing in patients with ocular trauma caused by enucleation of the eye[ J]. Chinese Journal of Woman and Child Health Research, 2017, 28(S3): 642-643.张津方, 周畅. 情绪安抚护理运用在眼外伤致眼球摘除术患者中的护理效果分析[ J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2017, 28(S3):642-643.
ZHANG Jinfang, ZHOU Chang. analysis of the effect of emotional comfort nursing in patients with ocular trauma caused by enucleation of the eye[ J]. Chinese Journal of Woman and Child Health Research, 2017, 28(S3): 642-643.