目的:探讨老年性糖尿病性白内障患者治疗及延续护理的措施。
方法:对2014年1月~2014年12月142例老年性糖尿病性白内障患者随机平均分为A组和B组,A组接受常规的出院指导;B组接受常规的出院指导及加强延续护理,根据老年性糖尿病性白内障患者
的具体情况制定护理措施 (眼部的护理、用药指导、饮食护理、心理护理、自我监测指导、定期随访及复查等内容),并进行跟踪处理。
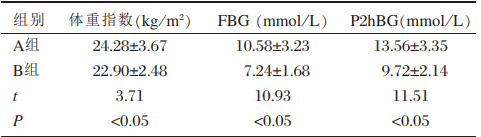
结果:实施延续护理一年后的患者,体重、空腹血糖、餐后2 h血糖与未实施延续护理的患者相比,差异有显著意义 (P<0.05)。
结论:护士对老年性糖尿病性白内障患者及家属进行用眼和糖尿病相关的知识宣教、针对性的心理护理、药物治疗护理及日常生活指导等,老年性糖尿病性白内障患者的遵医率提高,减少了因疾病而对生活工作的影响,生活质量有不同程度的提高。
Purpose: To explore the treatment and continuing nursing of patients diagnosed with senile and diabetic
cataract.
Methods: In total, 142 patients diagnosed with senile and diabetic cataract admitted to Zhongshan Ophthalmic
Center from January to December 2014 were randomly assigned into groups A and B. In group A, patients received conventional instruction after discharge, and those in group B additionally received continuing
nursing care after discharge including ocular nursing, use of anti-diabetic drugs, psychological
nursing, diet nursing, self-monitoring guidance, re-examination and regular follow-up according to the
patients’ conditions.
Results: After one year of continuing nursing care, visual acuity of patients in group B was increased
without complications. Body mass index, the fasting and 2h postprandial plasma glucose, and the systolic
and diastolic blood pressure were decreased significantly compared with those in group A (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: Continuing nursing care, including knowledge education related to ocular use and diabetes
mellitus, targeted psychological nursing, medication nursing and daily life guidance, play a pivotal role
in enhancing the compliance rate of the patients, reducing the influence upon work and life and enhancing
the quality of life to varying extent.