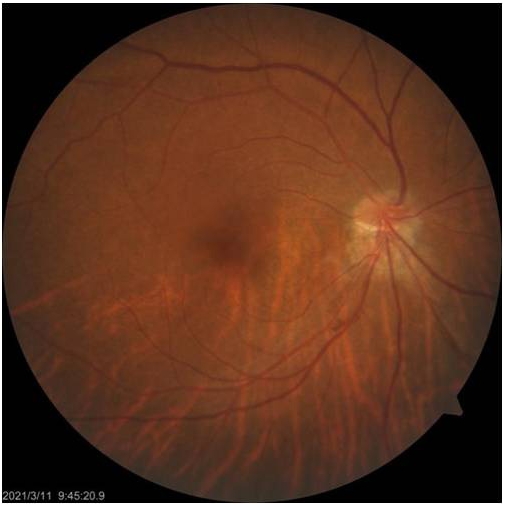
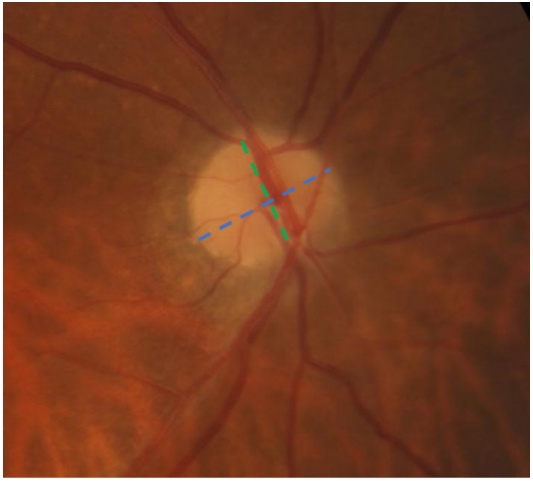
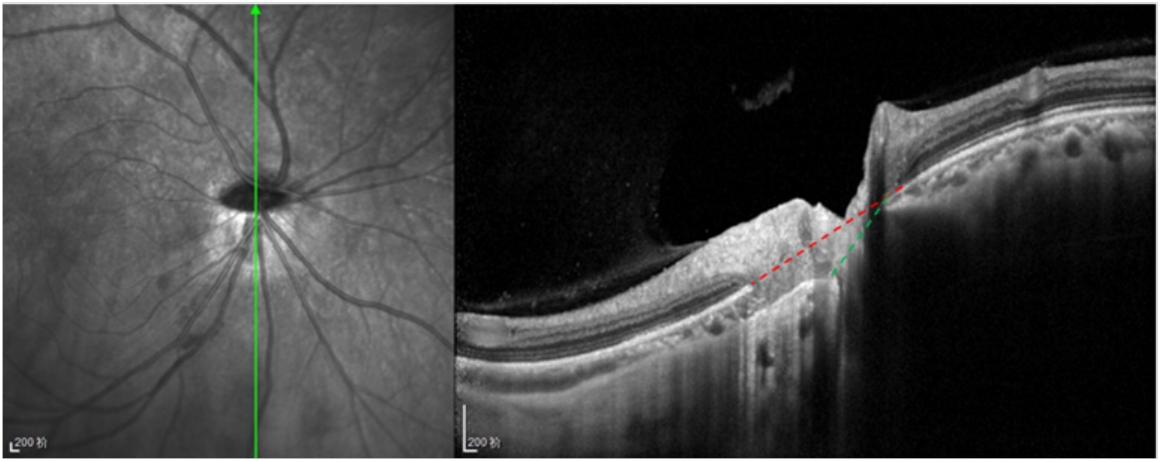
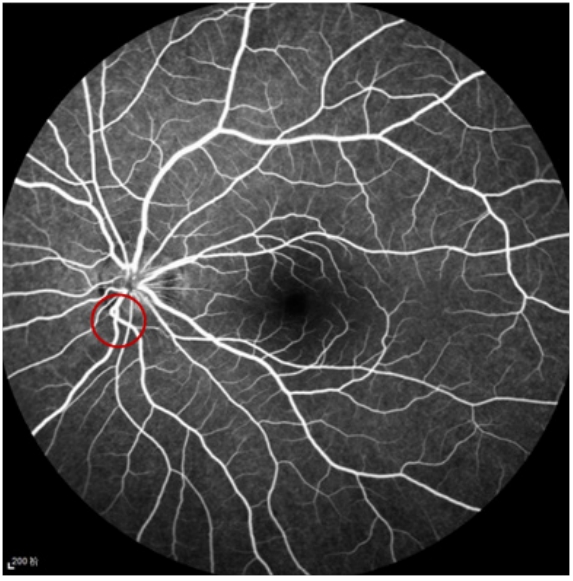
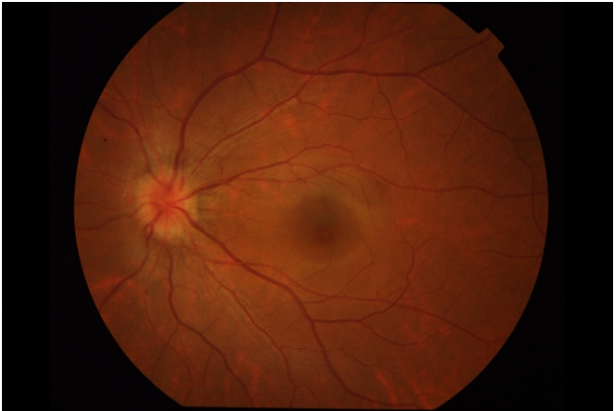
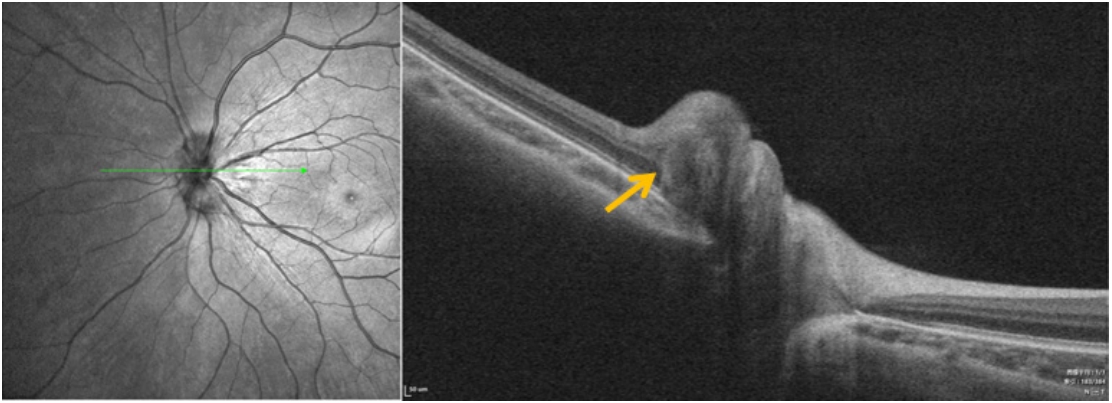
1、范媛媛, 魏文斌. 视盘倾斜及其相关性研究现状[ J]. 国际眼科纵
览, 2016, 40(2): 73-80. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673- 5803.2016.02.001.
Fan YY, Wei WB. Research progress on morphology and associations
of tilted optic disc[ J]. Int Rev Ophthalmol, 2016, 40(2): 73-80. DOI:
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-5803.2016.02.001.Fan YY, Wei WB. Research progress on morphology and associations
of tilted optic disc[ J]. Int Rev Ophthalmol, 2016, 40(2): 73-80. DOI:
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-5803.2016.02.001.
2、Apple DJ, Rabb MF, Walsh PM. Congenital anomalies of the optic
disc[ J]. Surv Ophthalmol, 1982, 27(1): 3-41. DOI:10.1016/0039-
6257(82)90111-4.Apple DJ, Rabb MF, Walsh PM. Congenital anomalies of the optic
disc[ J]. Surv Ophthalmol, 1982, 27(1): 3-41. DOI:10.1016/0039-
6257(82)90111-4.
3、Vongphanit J, Mitchell P, Wang JJ. Population prevalence of tilted optic disks and the relationship of this sign to refractive error[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol,
2002, 133(5): 679-685. DOI:10.1016/s0002-9394(02)01339-9.Vongphanit J, Mitchell P, Wang JJ. Population prevalence of tilted optic disks and the relationship of this sign to refractive error[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol,
2002, 133(5): 679-685. DOI:10.1016/s0002-9394(02)01339-9.
4、You QS, Xu L, Jonas JB. Tilted optic discs: the Beijing eye study[ J]. Eye,
2008, 22(5): 728-729. DOI:10.1038/eye.2008.87.You QS, Xu L, Jonas JB. Tilted optic discs: the Beijing eye study[ J]. Eye,
2008, 22(5): 728-729. DOI:10.1038/eye.2008.87.
5、Patyal S. Visual field defects with tilted and tortedoptic discs[M]//
Resolving Dilemmas in Perimetry.Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2021:
179-184. DOI:10.1007/978-981-16-2601-2_13.Patyal S. Visual field defects with tilted and tortedoptic discs[M]//
Resolving Dilemmas in Perimetry.Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2021:
179-184. DOI:10.1007/978-981-16-2601-2_13.
6、How ACS, Tan GSW, Chan YH, et al. Population prevalence of tilted
and torted optic discs among an adult Chinese population in Singapore:
the TanjongPagar Study[ J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 2009, 127(7): 894-899.
DOI:10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.134.How ACS, Tan GSW, Chan YH, et al. Population prevalence of tilted
and torted optic discs among an adult Chinese population in Singapore:
the TanjongPagar Study[ J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 2009, 127(7): 894-899.
DOI:10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.134.
7、Guo Y, Liu LJ, Xu L, et al. Optic disc ovality in primary school children
in Beijing[ J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2015, 56(8): 4547-4553. DOI:
10.1167/iovs.15-16590.Guo Y, Liu LJ, Xu L, et al. Optic disc ovality in primary school children
in Beijing[ J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2015, 56(8): 4547-4553. DOI:
10.1167/iovs.15-16590.
8、Orman%20G%2C%20Ayd%C4%B1noglu-Candan%20O%2C%20Sungur%20G.%20The%20prevalance%20of%20congenital%20%0Aoptic%20disc%20anomalies%20in%20Turkey%3A%20a%20hospital-based%20study%5BJ%5D.%20Int%20Ophthalmol%2C%20%0A2022%2C%2042(11)%3A%203567-3577.%20DOI%3A%2010.1007%2Fs10792-022-02357-8.Orman%20G%2C%20Ayd%C4%B1noglu-Candan%20O%2C%20Sungur%20G.%20The%20prevalance%20of%20congenital%20%0Aoptic%20disc%20anomalies%20in%20Turkey%3A%20a%20hospital-based%20study%5BJ%5D.%20Int%20Ophthalmol%2C%20%0A2022%2C%2042(11)%3A%203567-3577.%20DOI%3A%2010.1007%2Fs10792-022-02357-8.
9、Witmer MT, Margo CE, Drucker M. Tilted optic disks[ J]. Surv
Ophthalmol, 2010, 55(5): 403-428. DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.
2010.01.002.Witmer MT, Margo CE, Drucker M. Tilted optic disks[ J]. Surv
Ophthalmol, 2010, 55(5): 403-428. DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.
2010.01.002.
10、Giuffré G. Hypothesis on the pathogenesis of the papillary dysversion
syndrome[J]. J Fr Ophtalmol, 1985, 8(8-9): 565-572.Giuffré G. Hypothesis on the pathogenesis of the papillary dysversion
syndrome[J]. J Fr Ophtalmol, 1985, 8(8-9): 565-572.
11、杜芬, 罗俊, 向剑波, 等. 视盘倾斜综合征的视盘及屈光状态
观察[ J]. 临床眼科杂志, 2019, 27(4): 328-330. DOI: 10.3969/
j.issn.1006-8422.2019.04.011.
Du F, Luo J, Xiang JB, et al. Optic disc and refractive status in patients with
tilted disc syndrome[J]. J Clin Ophthalmol, 2019, 27(4): 328-330. DOI:
10.3969/j.issn.1006-8422.2019.04.011.Du F, Luo J, Xiang JB, et al. Optic disc and refractive status in patients with
tilted disc syndrome[J]. J Clin Ophthalmol, 2019, 27(4): 328-330. DOI:
10.3969/j.issn.1006-8422.2019.04.011.
12、Chan PP, Zhang Y, Pang CP. Myopic tilted disc: Mechanism, clinical
significance, and public health implication[ J]. Front Med, 2023, 10:
1094937. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1094937.Chan PP, Zhang Y, Pang CP. Myopic tilted disc: Mechanism, clinical
significance, and public health implication[ J]. Front Med, 2023, 10:
1094937. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1094937.
13、Dehghani C, Nowroozzadeh MH, Shankar S, et al. Ocular refractive
and biometric characteristics in patients with tilted disc syndrome[ J].
Optometry, 2010, 81(12): 688-694. DOI:10.1016/j.optm.2010.03.009.Dehghani C, Nowroozzadeh MH, Shankar S, et al. Ocular refractive
and biometric characteristics in patients with tilted disc syndrome[ J].
Optometry, 2010, 81(12): 688-694. DOI:10.1016/j.optm.2010.03.009.
14、Jonas JB, Kling F, Gründler AE. Optic disc shape, corneal astigmatism, and
amblyopia[J]. Ophthalmology, 1997, 104(11): 1934-1937. DOI:10.1016/
s0161-6420(97)30004-9.Jonas JB, Kling F, Gründler AE. Optic disc shape, corneal astigmatism, and
amblyopia[J]. Ophthalmology, 1997, 104(11): 1934-1937. DOI:10.1016/
s0161-6420(97)30004-9.
15、Lempert P, Porter L. Dysversion of the optic disc and axial length
measurements in a presumed amblyopic population[J]. J Am Assoc Pediatr
Ophthalmol Strabismus, 1998, 2(4): 207-213. DOI:10.1016/S1091-
8531(98)90054-4.Lempert P, Porter L. Dysversion of the optic disc and axial length
measurements in a presumed amblyopic population[J]. J Am Assoc Pediatr
Ophthalmol Strabismus, 1998, 2(4): 207-213. DOI:10.1016/S1091-
8531(98)90054-4.
16、Ju C, Widder J, Pham N. Tilted disc syndrome with bitemporal hemianopia
in a 67-year-old woman with high myopia and mixed/combined�mechanism glaucoma: areport of a rare case[ J]. UCLA Radiol Sci Proc,
2024, 4(3): 38-44. DOI: 10.5070/rs44353362.Ju C, Widder J, Pham N. Tilted disc syndrome with bitemporal hemianopia
in a 67-year-old woman with high myopia and mixed/combined�mechanism glaucoma: areport of a rare case[ J]. UCLA Radiol Sci Proc,
2024, 4(3): 38-44. DOI: 10.5070/rs44353362.
17、Phu J, Wang H, Miao S, et al. Neutralizing peripheral refraction eliminates
refractive scotomata in tilted disc syndrome[ J]. Optom Vis Sci, 2018,
95(10): 959-970. DOI: 10.1097/OPX. 0000000000001286.Phu J, Wang H, Miao S, et al. Neutralizing peripheral refraction eliminates
refractive scotomata in tilted disc syndrome[ J]. Optom Vis Sci, 2018,
95(10): 959-970. DOI: 10.1097/OPX. 0000000000001286.
18、Pichi F, Romano S, Villani E, et al. Spectral-domain optical coherence
tomography findings in pediatric tilted disc syndrome[ J]. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2014, 252(10): 1661-1667. DOI:10.1007/s00417-
014-2701-8.Pichi F, Romano S, Villani E, et al. Spectral-domain optical coherence
tomography findings in pediatric tilted disc syndrome[ J]. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2014, 252(10): 1661-1667. DOI:10.1007/s00417-
014-2701-8.
19、Giuffrè G. Chorioretinal degenerative changes in the tilted disc
syndrome[ J]. Int Ophthalmol, 1991, 15(1): 1-7. DOI:10.1007/
BF00150971.Giuffrè G. Chorioretinal degenerative changes in the tilted disc
syndrome[ J]. Int Ophthalmol, 1991, 15(1): 1-7. DOI:10.1007/
BF00150971.
20、Lee EJ, Han JC, Kee C. Deep optic nerve head morphology in tilted
disc syndrome and its clinical implication on visual damage[ J]. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2023, 64(13): 10. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.64.13.10.Lee EJ, Han JC, Kee C. Deep optic nerve head morphology in tilted
disc syndrome and its clinical implication on visual damage[ J]. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2023, 64(13): 10. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.64.13.10.
21、Yoon JY, Sung KR, Yun SC, et al. Progressive optic disc tilt in young myopic
glaucomatous eyes[ J]. Korean J Ophthalmol, 2019, 33(6): 520-527.
DOI:10.3341/kjo.2019.0069.Yoon JY, Sung KR, Yun SC, et al. Progressive optic disc tilt in young myopic
glaucomatous eyes[ J]. Korean J Ophthalmol, 2019, 33(6): 520-527.
DOI:10.3341/kjo.2019.0069.
22、Gediz%20B%C5%9E%2C%20Ali%20%C5%9Eekero%C4%9Flu%20M.%20Multimodal%20imaging%20in%20a%20case%20of%20fovea%20Plana%20%0Aassociated%20with%20situs%20inversus%20of%20the%20optic%20disc%5B%20J%5D.%20Turk%20J%20Ophthalmol%2C%20%0A2020%2C%2050(3)%3A%20190-192.%20DOI%3A%2010.4274%2Ftjo.galenos.2020.98415.Gediz%20B%C5%9E%2C%20Ali%20%C5%9Eekero%C4%9Flu%20M.%20Multimodal%20imaging%20in%20a%20case%20of%20fovea%20Plana%20%0Aassociated%20with%20situs%20inversus%20of%20the%20optic%20disc%5B%20J%5D.%20Turk%20J%20Ophthalmol%2C%20%0A2020%2C%2050(3)%3A%20190-192.%20DOI%3A%2010.4274%2Ftjo.galenos.2020.98415.
23、Adams MK, Cohen SY, Souied EH, et al. Multimodal imaging of choroidal
and optic disk vessels near optic disk pits[J]. Retin Cases Brief Rep, 2020,
14(4): 289-296. DOI:10.1097/ICB.0000000000000765.Adams MK, Cohen SY, Souied EH, et al. Multimodal imaging of choroidal
and optic disk vessels near optic disk pits[J]. Retin Cases Brief Rep, 2020,
14(4): 289-296. DOI:10.1097/ICB.0000000000000765.
24、Nghiem-Buffet S, Sibilia L, CohenSY. Tilted disc in eyes with fovea
Plana[J]. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2023, 261(11): 3159-3164.
DOI: 10.1007/s00417-023-06161-7.Nghiem-Buffet S, Sibilia L, CohenSY. Tilted disc in eyes with fovea
Plana[J]. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2023, 261(11): 3159-3164.
DOI: 10.1007/s00417-023-06161-7.
25、Denis D, Hugo J, Beylerian M, et al. Congenital abnormalities of the
optic disc[ J]. J Fr Ophtalmol, 2019, 42(7): 778-789. DOI:10.1016/
j.jfo.2018.09.011.Denis D, Hugo J, Beylerian M, et al. Congenital abnormalities of the
optic disc[ J]. J Fr Ophtalmol, 2019, 42(7): 778-789. DOI:10.1016/
j.jfo.2018.09.011.
26、Sibony PA, Kupersmith MJ, Kardon RH. Optical coherence tomography
neuro-toolbox for the diagnosis and management of papilledema, optic disc
edema, and pseudopapilledema[J]. J Neuroophthalmol, 2021, 41(1): 77-
92. DOI: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001078.Sibony PA, Kupersmith MJ, Kardon RH. Optical coherence tomography
neuro-toolbox for the diagnosis and management of papilledema, optic disc
edema, and pseudopapilledema[J]. J Neuroophthalmol, 2021, 41(1): 77-
92. DOI: 10.1097/WNO.0000000000001078.
27、Allegrini D, Pagano L, Ferrara M, et al. Optic disc drusen: a systematic
review: up-to-date and futureperspective[J]. Int Ophthalmol, 2020, 40(8):
2119-2127. DOI:10.1007/s10792-020-01365-w.Allegrini D, Pagano L, Ferrara M, et al. Optic disc drusen: a systematic
review: up-to-date and futureperspective[J]. Int Ophthalmol, 2020, 40(8):
2119-2127. DOI:10.1007/s10792-020-01365-w.
28、Martin-Gutierrez%20MP%2C%20Petzold%20A%2C%20Saihan%20Z.%20Correction%3A%20NAION%20or%20not%20%0ANAION%3F%20A%20literature%20review%20of%20pathogenesis%20and%20differential%20diagnosis%20of%20%0Aanterior%20ischaemic%20optic%20neuropathies%5B%20J%5D.%20Eye%20(Lond)%2C%202024%2C%2038(3)%3A%20631.%20%0ADOI%3A10.1038%2Fs41433-023-02873-6.Martin-Gutierrez%20MP%2C%20Petzold%20A%2C%20Saihan%20Z.%20Correction%3A%20NAION%20or%20not%20%0ANAION%3F%20A%20literature%20review%20of%20pathogenesis%20and%20differential%20diagnosis%20of%20%0Aanterior%20ischaemic%20optic%20neuropathies%5B%20J%5D.%20Eye%20(Lond)%2C%202024%2C%2038(3)%3A%20631.%20%0ADOI%3A10.1038%2Fs41433-023-02873-6.
29、Xie X, Liu T, Wang W, et al. Clinical and multi-mode imaging features of
eyes with peripapillaryhyperreflective ovoid mass-like structures[J]. Front
Med, 2022, 9: 796667.DOI:10.3389/fmed.2022.796667.Xie X, Liu T, Wang W, et al. Clinical and multi-mode imaging features of
eyes with peripapillaryhyperreflective ovoid mass-like structures[J]. Front
Med, 2022, 9: 796667.DOI:10.3389/fmed.2022.796667.
30、Chapman JJ, Heidary G, Gise R. An overview of peripapillaryhyperreflective
ovoid mass-like structures[J]. Curr Opin Ophthalmol, 2022, 33(6): 494-
500. DOI:10.1097/ICU.0000000000000897.Chapman JJ, Heidary G, Gise R. An overview of peripapillaryhyperreflective
ovoid mass-like structures[J]. Curr Opin Ophthalmol, 2022, 33(6): 494-
500. DOI:10.1097/ICU.0000000000000897.
31、Ly u I J, Park KA , Oh S Y. A ssociation bet ween myopia and
peripapillaryhyperreflective ovoid mass-like structures in children[ J]. Sci
Rep, 2020, 10(1): 2238. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-58829-3.Ly u I J, Park KA , Oh S Y. A ssociation bet ween myopia and
peripapillaryhyperreflective ovoid mass-like structures in children[ J]. Sci
Rep, 2020, 10(1): 2238. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-58829-3.
32、Borrelli E, Barboni P, Battista M, et al. Peripapillaryhyperreflective ovoid
mass-like structures (PHOMS): OCTA may reveal new findings[ J]. Eye,
2021, 35(2): 528-531. DOI:10.1038/s41433-020-0890-4.Borrelli E, Barboni P, Battista M, et al. Peripapillaryhyperreflective ovoid
mass-like structures (PHOMS): OCTA may reveal new findings[ J]. Eye,
2021, 35(2): 528-531. DOI:10.1038/s41433-020-0890-4.
33、王静, 刘佩, 吴松笛. 误诊为视神经炎的视盘倾斜综合征合并视
盘周围强反射卵圆形肿块样结构1例[ J]. 中华眼底病杂志, 2022,
38(5): 407-408. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511434-20210802-00412.
Wang J, Liu P, Wu SD. Chin J Ocul Fundus Dis, 2022, 38(5): 407-408.
DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511434-20210802-00412.Wang J, Liu P, Wu SD. Chin J Ocul Fundus Dis, 2022, 38(5): 407-408.
DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn511434-20210802-00412.
34、Kim MS, Hwang JM, Woo SJ. Long-term development and progression
of peripapillaryhyper-reflective ovoid mass-like structures: two case
reports[ J]. J Neuroophthalmol, 2022, 42(1): e352-e355. DOI:10.1097/
WNO.0000000000001366.Kim MS, Hwang JM, Woo SJ. Long-term development and progression
of peripapillaryhyper-reflective ovoid mass-like structures: two case
reports[ J]. J Neuroophthalmol, 2022, 42(1): e352-e355. DOI:10.1097/
WNO.0000000000001366.
35、Cohen SY, Dubois L, Nghiem-Buffet S, et al. Spectral domain optical
coherence tomography analysis of macular changes in tilted disk
syndrome[ J]. Retina, 2013, 33(7): 1338-1345. DOI:10.1097/
IAE.0b013e3182831364.Cohen SY, Dubois L, Nghiem-Buffet S, et al. Spectral domain optical
coherence tomography analysis of macular changes in tilted disk
syndrome[ J]. Retina, 2013, 33(7): 1338-1345. DOI:10.1097/
IAE.0b013e3182831364.
36、Garcia-Ben A,González Gómez A, García Basterra I, et al. Factors associated
with serous retinal detachment in highly myopic eyes with inferior posterior
staphyloma[ J]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol, 2020, 95(10): 478-484. DOI:
10.1016/j.oftal.2020.05.013.Garcia-Ben A,González Gómez A, García Basterra I, et al. Factors associated
with serous retinal detachment in highly myopic eyes with inferior posterior
staphyloma[ J]. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol, 2020, 95(10): 478-484. DOI:
10.1016/j.oftal.2020.05.013.
37、Kumar V, Surve A, Kumawat D, et al. Macular associations of tilted
disc syndrome[ J]. Indian J Ophthalmol, 2021, 69(6): 1451-1456.
DOI:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1902_20.Kumar V, Surve A, Kumawat D, et al. Macular associations of tilted
disc syndrome[ J]. Indian J Ophthalmol, 2021, 69(6): 1451-1456.
DOI:10.4103/ijo.IJO_1902_20.
38、Minowa Y, Ohkoshi K, Ozawa Y. Subthreshold laser treatment for serous
retinal detachment associated with tilted disc syndrome[ J]. Case Rep
Ophthalmol, 2021, 12(3): 978-986. DOI:10.1159/000520570.Minowa Y, Ohkoshi K, Ozawa Y. Subthreshold laser treatment for serous
retinal detachment associated with tilted disc syndrome[ J]. Case Rep
Ophthalmol, 2021, 12(3): 978-986. DOI:10.1159/000520570.
39、Kubota F, Suetsugu T, Kato A, et al. Tilted disc syndrome associated with
serous retinal detachment: long-term prognosis. A retrospective multicenter
survey[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2019, 207: 313-318. DOI:10.1016/
j.ajo.2019.05.027.Kubota F, Suetsugu T, Kato A, et al. Tilted disc syndrome associated with
serous retinal detachment: long-term prognosis. A retrospective multicenter
survey[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2019, 207: 313-318. DOI:10.1016/
j.ajo.2019.05.027.
40、Kathare R, Gandhi P, Prabhu V, et al. Posterior staphyloma-induced serous
maculopathy: evolution and successful treatment with subthreshold
micro pulse laser[ J]. Eur J Ophthalmol, 2024, 34(6): NP48-NP53.
DOI:10.1177/11206721241272249.Kathare R, Gandhi P, Prabhu V, et al. Posterior staphyloma-induced serous
maculopathy: evolution and successful treatment with subthreshold
micro pulse laser[ J]. Eur J Ophthalmol, 2024, 34(6): NP48-NP53.
DOI:10.1177/11206721241272249.
41、Mizuno H, Suzuki H, Mimura M, et al. Three cases of macular hole that
occurred in inferior scleral staphyloma associated with tilted disc syndrome:
a case series[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2022, 16(1): 36. DOI:10.1186/s13256-
022-03252-7.Mizuno H, Suzuki H, Mimura M, et al. Three cases of macular hole that
occurred in inferior scleral staphyloma associated with tilted disc syndrome:
a case series[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2022, 16(1): 36. DOI:10.1186/s13256-
022-03252-7.
42、Shinohara K, Tanaka N, Jonas JB, et al. Ultrawide-field OCT to
investigate relationships between myopic macular retinoschisis and
posterior staphyloma[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2018, 125(10): 1575-1586.
DOI:10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.03.053.Shinohara K, Tanaka N, Jonas JB, et al. Ultrawide-field OCT to
investigate relationships between myopic macular retinoschisis and
posterior staphyloma[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2018, 125(10): 1575-1586.
DOI:10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.03.053.
43、Ikuno Y. Overview of the complications of high myopia[J]. Retina, 2017,
37(12): 2347-2351. DOI:10.1097/IAE.0000000000001489.Ikuno Y. Overview of the complications of high myopia[J]. Retina, 2017,
37(12): 2347-2351. DOI:10.1097/IAE.0000000000001489.
44、Bando H, Ikuno Y, Choi JS, et al. Ultrastructure of internal limiting
membrane in myopic foveoschisis[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2005, 139(1):
197-199. DOI:10.1016/j.ajo.2004.07.027.Bando H, Ikuno Y, Choi JS, et al. Ultrastructure of internal limiting
membrane in myopic foveoschisis[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2005, 139(1):
197-199. DOI:10.1016/j.ajo.2004.07.027.
45、Cohen SY, Vignal-Clermont C, Trinh L, et al. Tilted disc syndrome (TDS):
new hypotheses for posterior segment complications and their implications
in other retinal diseases[ J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2022, 88: 101020.
DOI:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101020.Cohen SY, Vignal-Clermont C, Trinh L, et al. Tilted disc syndrome (TDS):
new hypotheses for posterior segment complications and their implications
in other retinal diseases[ J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2022, 88: 101020.
DOI:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101020.
46、Cohen SY, Dubois L, Ayrault S, et al. T-shaped pigmentary changes
in tilted disk syndrome[ J]. Eur J Ophthalmol, 2009, 19(5): 876-879.
DOI:10.1177/112067210901900532.Cohen SY, Dubois L, Ayrault S, et al. T-shaped pigmentary changes
in tilted disk syndrome[ J]. Eur J Ophthalmol, 2009, 19(5): 876-879.
DOI:10.1177/112067210901900532.