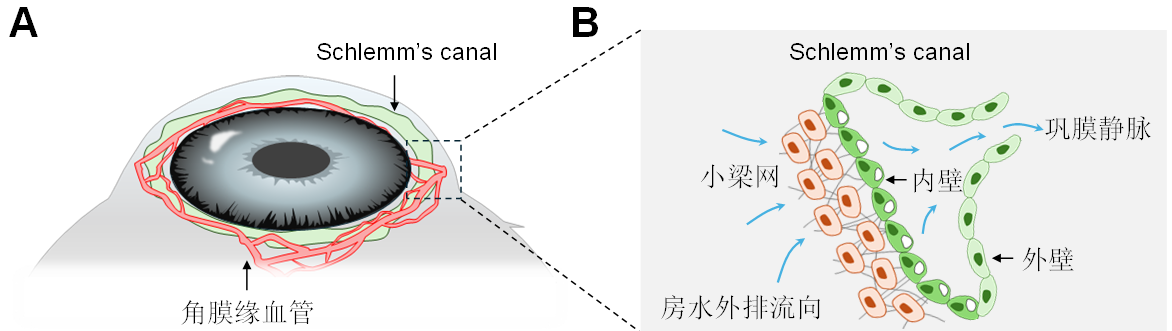
1、Hamanaka%20T%2C%20Ujike%20K.%20%5BThree-dimensional%20structure%20of%20Schlemm's%20canal%20(author's%20transl)%5D%5BJ%5D.%20Nippon%20Ganka%20Gakkai%20Zasshi%2C%201980%2C%2084(9)%3A1292-304.%C2%A0Hamanaka%20T%2C%20Ujike%20K.%20%5BThree-dimensional%20structure%20of%20Schlemm's%20canal%20(author's%20transl)%5D%5BJ%5D.%20Nippon%20Ganka%20Gakkai%20Zasshi%2C%201980%2C%2084(9)%3A1292-304.%C2%A0
2、Johnson M, McLaren JW, Overby DR. Unconventional aqueous humor outflow: a review[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2017, 158: 94-111. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.01.017. Johnson M, McLaren JW, Overby DR. Unconventional aqueous humor outflow: a review[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2017, 158: 94-111. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.01.017.
3、Gabelt BT, Kaufman PL. Changes in aqueous humor dynamics with age and glaucoma[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2005, 24(5): 612-637. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2004.10.003. Gabelt BT, Kaufman PL. Changes in aqueous humor dynamics with age and glaucoma[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2005, 24(5): 612-637. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2004.10.003.
4、Ramos%20RF%2C%20Hoying%20JB%2C%20Witte%20MH%2C%20et%20al.%20Schlemm%E2%80%99s%20canal%20endothelia%2C%20lymphatic%2C%20or%20blood%20vasculature%3F%5BJ%5D.%20J%20Glaucoma%2C%202007%2C%2016(4)%3A%20391-405.%20DOI%3A%2010.1097%2FIJG.0b013e3180654ac6.%20Ramos%20RF%2C%20Hoying%20JB%2C%20Witte%20MH%2C%20et%20al.%20Schlemm%E2%80%99s%20canal%20endothelia%2C%20lymphatic%2C%20or%20blood%20vasculature%3F%5BJ%5D.%20J%20Glaucoma%2C%202007%2C%2016(4)%3A%20391-405.%20DOI%3A%2010.1097%2FIJG.0b013e3180654ac6.%20
5、Stamer WD, Braakman ST, Zhou EH, et al. Biomechanics of Schlemm’s canal endothelium and intraocular pressure reduction[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2015, 44: 86-98. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.08.002. Stamer WD, Braakman ST, Zhou EH, et al. Biomechanics of Schlemm’s canal endothelium and intraocular pressure reduction[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2015, 44: 86-98. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.08.002.
6、Tham YC, Li X, Wong T, et al. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Ophthalmology, 2014, 121(11):2081-90. DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.05.013. Tham YC, Li X, Wong T, et al. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Ophthalmology, 2014, 121(11):2081-90. DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.05.013.
7、Acott TS, Vranka JA, Keller KE, et al. Normal and glaucomatous outflow regulation[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2021, 82: 100897. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100897. Acott TS, Vranka JA, Keller KE, et al. Normal and glaucomatous outflow regulation[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2021, 82: 100897. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100897.
8、Dautriche CN, Tian Y, Xie Y, et al. A closer look at schlemm’s canal cell physiology: implications for biomimetics[J]. J Funct Biomater, 2015, 6(3): 963-985. DOI: 10.3390/jfb6030963. Dautriche CN, Tian Y, Xie Y, et al. A closer look at schlemm’s canal cell physiology: implications for biomimetics[J]. J Funct Biomater, 2015, 6(3): 963-985. DOI: 10.3390/jfb6030963.
9、Mansouri K, Shaarawy T. Update on Schlemm’s canal based procedures[J]. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol, 2015, 22(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.4103/0974-9233.148347. Mansouri K, Shaarawy T. Update on Schlemm’s canal based procedures[J]. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol, 2015, 22(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.4103/0974-9233.148347.
10、Wang LY, Su GY, Wei ZY, et al. Progress in the basic and clinical research on the Schlemm’s canal[J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2020, 13(5): 816-821. DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2020.05.18.Wang LY, Su GY, Wei ZY, et al. Progress in the basic and clinical research on the Schlemm’s canal[J]. Int J Ophthalmol, 2020, 13(5): 816-821. DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2020.05.18.
11、Dautriche CN, Szymanski D, Kerr M, et al. A biomimetic Schlemm’s canal inner wall: a model to study outflow physiology, glaucoma pathology and high-throughput drug screening[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 65: 86-92. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.06.034.Dautriche CN, Szymanski D, Kerr M, et al. A biomimetic Schlemm’s canal inner wall: a model to study outflow physiology, glaucoma pathology and high-throughput drug screening[J]. Biomaterials, 2015, 65: 86-92. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.06.034.
12、Lewczuk%20K%2C%20Jab%C5%82o%C5%84ska%20J%2C%20Konopi%C5%84ska%20J%2C%20et%20al.%20Schlemm%E2%80%99s%20canal%3A%20the%20outflow%20'vessel'%5BJ%5D.%20Acta%20Ophthalmol%2C%202022%2C%20100(4)%3A%20e881-e890.%20DOI%3A%2010.1111%2Faos.15027.Lewczuk%20K%2C%20Jab%C5%82o%C5%84ska%20J%2C%20Konopi%C5%84ska%20J%2C%20et%20al.%20Schlemm%E2%80%99s%20canal%3A%20the%20outflow%20'vessel'%5BJ%5D.%20Acta%20Ophthalmol%2C%202022%2C%20100(4)%3A%20e881-e890.%20DOI%3A%2010.1111%2Faos.15027.
13、Ethier CR. The inner wall of Schlemm’s canal[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2002, 74(2): 161-172. DOI: 10.1006/exer.2002.1144. Ethier CR. The inner wall of Schlemm’s canal[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2002, 74(2): 161-172. DOI: 10.1006/exer.2002.1144.
14、Epstein DL, Rohen JW. Morphology of the trabecular meshwork and inner-wall endothelium after cationized ferritin perfusion in the monkey eye[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 1991, 32(1): 160-171. Epstein DL, Rohen JW. Morphology of the trabecular meshwork and inner-wall endothelium after cationized ferritin perfusion in the monkey eye[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 1991, 32(1): 160-171.
15、Ethier CR, Coloma FM, Sit AJ, et al. Two pore types in the inner-wall endothelium of Schlemm’s canal[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 1998, 39(11): 2041-2048. Ethier CR, Coloma FM, Sit AJ, et al. Two pore types in the inner-wall endothelium of Schlemm’s canal[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 1998, 39(11): 2041-2048.
16、Braakman ST, Pedrigi RM, Read AT, et al. Biomechanical strain as a trigger for pore formation in Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2014, 127: 224-235. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.08.003. Braakman ST, Pedrigi RM, Read AT, et al. Biomechanical strain as a trigger for pore formation in Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2014, 127: 224-235. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.08.003.
17、Vahabikashi A, Gelman A, Dong B, et al. Increased stiffness and flow resistance of the inner wall of Schlemm’s canal in glaucomatous human eyes[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116(52): 26555-26563. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1911837116.Vahabikashi A, Gelman A, Dong B, et al. Increased stiffness and flow resistance of the inner wall of Schlemm’s canal in glaucomatous human eyes[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116(52): 26555-26563. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1911837116.
18、Battista SA, Lu Z, Hofmann S, et al. Reduction of the available area for aqueous humor outflow and increase in meshwork herniations into collector channels following acute IOP elevation in bovine eyes[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2008, 49(12): 5346-5352. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.08-1707. Battista SA, Lu Z, Hofmann S, et al. Reduction of the available area for aqueous humor outflow and increase in meshwork herniations into collector channels following acute IOP elevation in bovine eyes[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2008, 49(12): 5346-5352. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.08-1707.
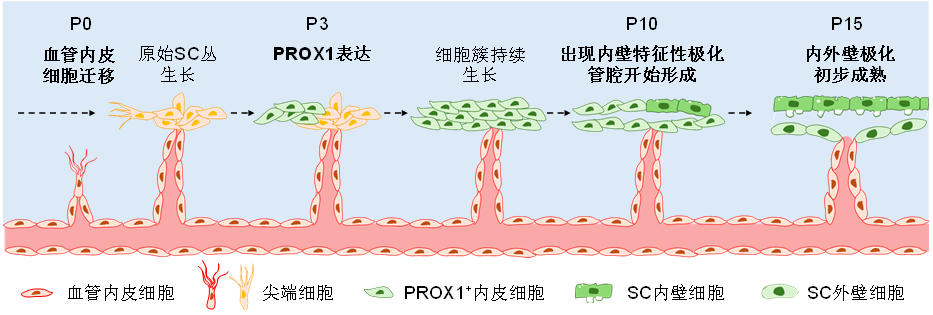
19、Ramírez JM, Ramírez AI, Salazar JJ, et al. Schlemm’s canal and the collector channels at different developmental stages in the human eye[J]. Cells Tissues Organs, 2004, 178(3): 180-185. DOI: 10.1159/000082248.Ramírez JM, Ramírez AI, Salazar JJ, et al. Schlemm’s canal and the collector channels at different developmental stages in the human eye[J]. Cells Tissues Organs, 2004, 178(3): 180-185. DOI: 10.1159/000082248.
20、Kizhatil K, Ryan M, Marchant JK, et al. Schlemm’s canal is a unique vessel with a combination of blood vascular and lymphatic phenotypes that forms by a novel developmental process[J]. PLoS Biol, 2014, 12(7): e1001912. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001912. Kizhatil K, Ryan M, Marchant JK, et al. Schlemm’s canal is a unique vessel with a combination of blood vascular and lymphatic phenotypes that forms by a novel developmental process[J]. PLoS Biol, 2014, 12(7): e1001912. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001912.
21、Park DY, Lee J, Park I, et al. Lymphatic regulator PROX1 determines Schlemm’s canal integrity and identity[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(9): 3960-3974. DOI: 10.1172/jci75392. Park DY, Lee J, Park I, et al. Lymphatic regulator PROX1 determines Schlemm’s canal integrity and identity[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(9): 3960-3974. DOI: 10.1172/jci75392.
22、Aspelund A, Tammela T, Antila S, et al. The Schlemm’s canal is a VEGF-C/VEGFR-3-responsive lymphatic-like vessel[J]. J Clin Investig, 2014, 124(9): 3975-3986. DOI: 10.1172/JCI75395.Aspelund A, Tammela T, Antila S, et al. The Schlemm’s canal is a VEGF-C/VEGFR-3-responsive lymphatic-like vessel[J]. J Clin Investig, 2014, 124(9): 3975-3986. DOI: 10.1172/JCI75395.
23、Johnstone%20M%2C%20Xin%20C%2C%20Tan%20J%2C%20et%20al.%20Aqueous%20outflow%20regulation%20-%2021st%20century%20concepts%5BJ%5D.%20Prog%20Retin%20Eye%20Res%2C%202021%2C83%3A100917.%20DOI%3A%2010.1016%2Fj.preteyeres.2020.100917.%C2%A0Johnstone%20M%2C%20Xin%20C%2C%20Tan%20J%2C%20et%20al.%20Aqueous%20outflow%20regulation%20-%2021st%20century%20concepts%5BJ%5D.%20Prog%20Retin%20Eye%20Res%2C%202021%2C83%3A100917.%20DOI%3A%2010.1016%2Fj.preteyeres.2020.100917.%C2%A0
24、Cha EDK, Xu J, Gong L, et al. Variations in active outflow along the trabecular outflow pathway[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2016, 146: 354-360. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.01.008. Cha EDK, Xu J, Gong L, et al. Variations in active outflow along the trabecular outflow pathway[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2016, 146: 354-360. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2016.01.008.
25、Keller KE, Bradley JM, Vranka JA, et al. Segmental versican expression in the trabecular meshwork and involvement in outflow facility[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2011, 52(8): 5049. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-6948. Keller KE, Bradley JM, Vranka JA, et al. Segmental versican expression in the trabecular meshwork and involvement in outflow facility[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2011, 52(8): 5049. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-6948.
26、Lu Z, Overby DR, Scott PA, et al. The mechanism of increasing outflow facility by rho-kinase inhibition with Y-27632 in bovine eyes[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2008, 86(2): 271-281. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.10.018. Lu Z, Overby DR, Scott PA, et al. The mechanism of increasing outflow facility by rho-kinase inhibition with Y-27632 in bovine eyes[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2008, 86(2): 271-281. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.10.018.
27、Lu Z, Zhang Y, Freddo TF, et al. Similar hydrodynamic and morphological changes in the aqueous humor outflow pathway after washout and Y27632 treatment in monkey eyes[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2011, 93(4): 397-404. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2011.05.012. Lu Z, Zhang Y, Freddo TF, et al. Similar hydrodynamic and morphological changes in the aqueous humor outflow pathway after washout and Y27632 treatment in monkey eyes[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2011, 93(4): 397-404. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2011.05.012.
28、Zhang Y, Toris CB, Liu Y, et al. Morphological and hydrodynamic correlates in monkey eyes with laser induced glaucoma[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2009, 89(5): 748-756. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.06.015. Zhang Y, Toris CB, Liu Y, et al. Morphological and hydrodynamic correlates in monkey eyes with laser induced glaucoma[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2009, 89(5): 748-756. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2009.06.015.
29、Johnstone M, Martin E, Jamil A. Pulsatile flow into the aqueous veins: manifestations in normal and glaucomatous eyes[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2011, 92(5): 318-327. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2011.03.011. Johnstone M, Martin E, Jamil A. Pulsatile flow into the aqueous veins: manifestations in normal and glaucomatous eyes[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2011, 92(5): 318-327. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2011.03.011.
30、Zhou EH, Krishnan R, Stamer WD, et al. Mechanical responsiveness of the endothelial cell of Schlemm’s canal: scope, variability and its potential role in controlling aqueous humour outflow[J]. J R Soc Interface, 2012, 9(71): 1144-1155. DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2011.0733. Zhou EH, Krishnan R, Stamer WD, et al. Mechanical responsiveness of the endothelial cell of Schlemm’s canal: scope, variability and its potential role in controlling aqueous humour outflow[J]. J R Soc Interface, 2012, 9(71): 1144-1155. DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2011.0733.
31、Ding X, Huang L, Peng C, et al. Evaluation of Schlemm’s canal with swept-source optical coherence tomography in primary angle-closure disease[J]. BMC Ophthalmol, 2023, 23(1): 256. DOI: 10.1186/s12886-023-03001-4.Ding X, Huang L, Peng C, et al. Evaluation of Schlemm’s canal with swept-source optical coherence tomography in primary angle-closure disease[J]. BMC Ophthalmol, 2023, 23(1): 256. DOI: 10.1186/s12886-023-03001-4.
32、Gonzalez JM, Ko MK, Hong YK, et al. Deep tissue analysis of distal aqueous drainage structures and contractile features[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 17071. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-16897-y. Gonzalez JM, Ko MK, Hong YK, et al. Deep tissue analysis of distal aqueous drainage structures and contractile features[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 17071. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-16897-y.
33、 Karpinich NO, Caron KM. Schlemm’s canal: more than meets the eye, lymphatics in disguise[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(9): 3701-3703. DOI: 10.1172/JCI77507. Karpinich NO, Caron KM. Schlemm’s canal: more than meets the eye, lymphatics in disguise[J]. J Clin Invest, 2014, 124(9): 3701-3703. DOI: 10.1172/JCI77507.
34、Reina-Torres E, Wen JC, Liu KC, et al. VEGF as a paracrine regulator of conventional outflow facility[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2017, 58(3): 1899-1908. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.16-20779. Reina-Torres E, Wen JC, Liu KC, et al. VEGF as a paracrine regulator of conventional outflow facility[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2017, 58(3): 1899-1908. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.16-20779.
35、Thomson BR, Souma T, Tompson SW, et al. Angiopoietin-1 is required for Schlemm's canal development in mice and humans[J]. J Clin Invest, 2017, 127(12):4421-4436. DOI: 10.1172/JCI95545.Thomson BR, Souma T, Tompson SW, et al. Angiopoietin-1 is required for Schlemm's canal development in mice and humans[J]. J Clin Invest, 2017, 127(12):4421-4436. DOI: 10.1172/JCI95545.
36、Souma T, Tompson SW, Thomson BR, et al. Angiopoietin receptor TEK mutations underlie primary congenital glaucoma with variable expressivity[J]. J Clin Investig, 2016, 126(7): 2575-2587. DOI: 10.1172/jci85830. Souma T, Tompson SW, Thomson BR, et al. Angiopoietin receptor TEK mutations underlie primary congenital glaucoma with variable expressivity[J]. J Clin Investig, 2016, 126(7): 2575-2587. DOI: 10.1172/jci85830.
37、Seegar TCM, Eller B, Tzvetkova-Robev D, et al. Tie1-Tie2 interactions mediate functional differences between angiopoietin ligands[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 37(5): 643-655. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.02.007. Seegar TCM, Eller B, Tzvetkova-Robev D, et al. Tie1-Tie2 interactions mediate functional differences between angiopoietin ligands[J]. Mol Cell, 2010, 37(5): 643-655. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.02.007.
38、Puri MC, Rossant J, Alitalo K, et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase TIE is required for integrity and survival of vascular endothelial cells[J]. EMBO J, 1995, 14(23): 5884-5891. DOI: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00276.x. Puri MC, Rossant J, Alitalo K, et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase TIE is required for integrity and survival of vascular endothelial cells[J]. EMBO J, 1995, 14(23): 5884-5891. DOI: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00276.x.
39、Du J, Thomson BR, Onay T, et al. Endothelial tyrosine kinase Tie1 is required for normal schlemm’s canal development-brief report[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2022, 42(3): 348-351. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316692. Du J, Thomson BR, Onay T, et al. Endothelial tyrosine kinase Tie1 is required for normal schlemm’s canal development-brief report[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2022, 42(3): 348-351. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316692.
40、Kechagia JZ, Ivaska J, Roca-Cusachs P. Integrins as biomechanical sensors of the microenvironment[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 20(8): 457-473. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-019-0134-2. Kechagia JZ, Ivaska J, Roca-Cusachs P. Integrins as biomechanical sensors of the microenvironment[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2019, 20(8): 457-473. DOI: 10.1038/s41580-019-0134-2.
41、 Narayanaswamy A, Thakur S, Nongpiur ME, et al. Aqueous outflow channels and its lymphatic association: a review[J]. Surv Ophthalmol, 2022, 67(3): 659-674. DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2021.10.004. Narayanaswamy A, Thakur S, Nongpiur ME, et al. Aqueous outflow channels and its lymphatic association: a review[J]. Surv Ophthalmol, 2022, 67(3): 659-674. DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2021.10.004.
42、Gu X, Chen X, Zhang X, et al. Macrophage-induced integrin signaling promotes Schlemm’s canal formation to prevent intraocular hypertension and glaucomatous optic neuropathy[J]. Cell Rep, 2024, 43(2): 113799. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113799. Gu X, Chen X, Zhang X, et al. Macrophage-induced integrin signaling promotes Schlemm’s canal formation to prevent intraocular hypertension and glaucomatous optic neuropathy[J]. Cell Rep, 2024, 43(2): 113799. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113799.
43、Kiyota N, Thomson B, Zhou Y, et al. The Impact of ITGA9 on Schlemm's Canal Formation in Mice[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2024, 65(7): 4260.Kiyota N, Thomson B, Zhou Y, et al. The Impact of ITGA9 on Schlemm's Canal Formation in Mice[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2024, 65(7): 4260.
44、Baneyx G, Baugh L, Vogel V. Fibronectin extension and unfolding within cell matrix fibrils controlled by cytoskeletal tension[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(8): 5139-5143. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.072650799.Baneyx G, Baugh L, Vogel V. Fibronectin extension and unfolding within cell matrix fibrils controlled by cytoskeletal tension[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(8): 5139-5143. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.072650799.
45、Kelly RA, Perkumas KM, Campbell M, et al. Fibrotic changes to schlemm’s canal endothelial cells in glaucoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9446. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179446.Kelly RA, Perkumas KM, Campbell M, et al. Fibrotic changes to schlemm’s canal endothelial cells in glaucoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(17): 9446. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179446.
46、Ellis DZ, Sharif NA, Dismuke WM. Endogenous regulation of human schlemm’s canal cell volume by nitric oxide signaling[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2010, 51(11): 5817. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-5072. Ellis DZ, Sharif NA, Dismuke WM. Endogenous regulation of human schlemm’s canal cell volume by nitric oxide signaling[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2010, 51(11): 5817. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.09-5072.
47、Ashpole NE, Overby DR, Ethier CR, et al. Shear stress-triggered nitric oxide release from schlemm’s canal cells[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2014, 55(12): 8067-8076. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.14-14722.Ashpole NE, Overby DR, Ethier CR, et al. Shear stress-triggered nitric oxide release from schlemm’s canal cells[J]. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2014, 55(12): 8067-8076. DOI: 10.1167/iovs.14-14722.
48、Dismuke WM, Liang J, Overby DR, et al. Concentration-related effects of nitric oxide and endothelin-1 on human trabecular meshwork cell contractility[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2014, 120: 28-35. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.12.012.Dismuke WM, Liang J, Overby DR, et al. Concentration-related effects of nitric oxide and endothelin-1 on human trabecular meshwork cell contractility[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2014, 120: 28-35. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.12.012.
49、Reina-Torres%20E%2C%20De%20Ieso%20ML%2C%20Pasquale%20L%2C%20et%20al.%20The%20vital%20role%20for%20nitric%20oxide%20in%20intraocular%20pressure%20homeostasis%5BJ%5D.%20Prog%20Retin%20Eye%20Res%2C%202021%2C%2083%3A100922.%20doi%3A%2010.1016%2Fj.preteyeres.2020.100922.%C2%A0Reina-Torres%20E%2C%20De%20Ieso%20ML%2C%20Pasquale%20L%2C%20et%20al.%20The%20vital%20role%20for%20nitric%20oxide%20in%20intraocular%20pressure%20homeostasis%5BJ%5D.%20Prog%20Retin%20Eye%20Res%2C%202021%2C%2083%3A100922.%20doi%3A%2010.1016%2Fj.preteyeres.2020.100922.%C2%A0
50、McDonnell F, Perkumas KM, Ashpole NE, et al. Shear stress in schlemm’s canal as a sensor of intraocular pressure[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 5804. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-62730-4. McDonnell F, Perkumas KM, Ashpole NE, et al. Shear stress in schlemm’s canal as a sensor of intraocular pressure[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 5804. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-62730-4.
51、国家眼部疾病临床医学研究中心青光眼协作组. 穿透性Schlemm管成形术围手术期管理专家共识 (2022)[J]. 中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志,2023,25(5):321-326, DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn115909-20230114-00013 (2023).
Glaucoma Collaborative Group of National Clinical Research Center for Ocular Diseases. Expert Consensus on Perioperative Management of Penetrating Canaloplasty (2022) [J]. Chinese Journal of Optometry Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 2023, 25(5): 321-326, DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115909-20230114-00013 (2023).Glaucoma Collaborative Group of National Clinical Research Center for Ocular Diseases. Expert Consensus on Perioperative Management of Penetrating Canaloplasty (2022) [J]. Chinese Journal of Optometry Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 2023, 25(5): 321-326, DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115909-20230114-00013 (2023).
52、Kopczynski CC, Epstein DL. Emerging trabecular outflow drugs[J]. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 30(2-3): 85-87. DOI: 10.1089/jop.2013.0197.Kopczynski CC, Epstein DL. Emerging trabecular outflow drugs[J]. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther, 2014, 30(2-3): 85-87. DOI: 10.1089/jop.2013.0197.
53、Ichioka H, Ida Y, Watanabe M, et al. Prostaglandin F2α and EP2 agonists, and a ROCK inhibitor modulate the formation of 3D organoids of Grave’s orbitopathy related human orbital fibroblasts[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2021, 205: 108489. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108489. Ichioka H, Ida Y, Watanabe M, et al. Prostaglandin F2α and EP2 agonists, and a ROCK inhibitor modulate the formation of 3D organoids of Grave’s orbitopathy related human orbital fibroblasts[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2021, 205: 108489. DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108489.
54、Al-Humimat G, Marashdeh I, Daradkeh D, et al. Investigational rho kinase inhibitors for the treatment of glaucoma[J]. J Exp Pharmacol, 2021, 13: 197-212. DOI: 10.2147/JEP.S259297. Al-Humimat G, Marashdeh I, Daradkeh D, et al. Investigational rho kinase inhibitors for the treatment of glaucoma[J]. J Exp Pharmacol, 2021, 13: 197-212. DOI: 10.2147/JEP.S259297.
55、Andrés-Guerrero V, García-Feijoo J, Konstas AG. Targeting schlemm’s canal in the medical therapy of glaucoma: current and future considerations[J]. Adv Ther, 2017, 34(5): 1049-1069. DOI: 10.1007/s12325-017-0513-z. Andrés-Guerrero V, García-Feijoo J, Konstas AG. Targeting schlemm’s canal in the medical therapy of glaucoma: current and future considerations[J]. Adv Ther, 2017, 34(5): 1049-1069. DOI: 10.1007/s12325-017-0513-z.
56、Fujimoto T, Inoue-Mochita M, Inoue T. A ROCK inhibitor suppresses the transforming growth factor-beta-2-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition in Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 9655. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36808-8. Fujimoto T, Inoue-Mochita M, Inoue T. A ROCK inhibitor suppresses the transforming growth factor-beta-2-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition in Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 9655. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36808-8.
57、Testa V, Ferro Desideri L, Della Giustina P, et al. An update on ripasudil for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension[J]. Drugs Today, 2020, 56(9): 599-608. DOI: 10.1358/dot.2020.56.9.3178110. Testa V, Ferro Desideri L, Della Giustina P, et al. An update on ripasudil for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension[J]. Drugs Today, 2020, 56(9): 599-608. DOI: 10.1358/dot.2020.56.9.3178110.
58、Fan W, Song M, Li L, et al. Endogenous dual stimuli-activated NO generation in the conventional outflow pathway for precision glaucoma therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 277: 121074. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121074. Fan W, Song M, Li L, et al. Endogenous dual stimuli-activated NO generation in the conventional outflow pathway for precision glaucoma therapy[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 277: 121074. DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121074.