1、Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, et al. IgG4-related disease[J]. Lancet, 2015, 385(9976): 1460-1471. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60720-0. Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, et al. IgG4-related disease[J]. Lancet, 2015, 385(9976): 1460-1471. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60720-0.
2、Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012, 64(10): 3061-3067. DOI:10.1002/art.34593. Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2012, 64(10): 3061-3067. DOI:10.1002/art.34593.
3、Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2012, 22(1): 1-14. DOI:10.1007/s10165-011-0508-6.Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2012, 22(1): 1-14. DOI:10.1007/s10165-011-0508-6.
4、中华医学会眼科学分会眼整形眼眶病学组, 中华医学会风湿病学分会. IgG4相关眼病诊治专家共识(2024版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2024, 104(40): 3726-3735. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20240814-01870.
Oculoplastic and Orbital Disease Group of Chinese Ophthalmological Society of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Rheumatology Association. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of immunoglobulin-G4 related ophthalmic disease (2024 edition)[J]. Natl Med J China, 2024, 104(40): 3726-3735. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20240814-01870.Oculoplastic and Orbital Disease Group of Chinese Ophthalmological Society of Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Rheumatology Association. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of immunoglobulin-G4 related ophthalmic disease (2024 edition)[J]. Natl Med J China, 2024, 104(40): 3726-3735. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20240814-01870.
5、Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. Pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2011, 23(1): 114-118. DOI:10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283412f4a.Zen Y, Nakanuma Y. Pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2011, 23(1): 114-118. DOI:10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283412f4a.
6、Rose NR. Autoimmune diseases: tracing the shared threads[J]. Hosp Pract, 1997, 32(4): 147-154. DOI:10.1080/21548331.1997.11443469.Rose NR. Autoimmune diseases: tracing the shared threads[J]. Hosp Pract, 1997, 32(4): 147-154. DOI:10.1080/21548331.1997.11443469.
7、Sun H, Zeng X, Li Y, et al. Successful remission induction of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease by obinutuzumab therapy: a retrospective study of 8 patients[J]. Eye, 2024, 38(4): 723-729. DOI:10.1038/s41433-023-02758-8.Sun H, Zeng X, Li Y, et al. Successful remission induction of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease by obinutuzumab therapy: a retrospective study of 8 patients[J]. Eye, 2024, 38(4): 723-729. DOI:10.1038/s41433-023-02758-8.
8、Wu A, Andrew NH, Tsirbas A, et al. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related orbital disease: experience from five cases[J]. Eye, 2015, 29(1): 122-128. DOI:10.1038/eye.2014.251.Wu A, Andrew NH, Tsirbas A, et al. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related orbital disease: experience from five cases[J]. Eye, 2015, 29(1): 122-128. DOI:10.1038/eye.2014.251.
9、Lu C, Li S, Qing P, et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis and protein profiling reveal broad immune system activation in IgG4-related disease[J]. JCI Insight, 2023, 8(17): e167602. DOI:10.1172/jci.insight.167602.Lu C, Li S, Qing P, et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis and protein profiling reveal broad immune system activation in IgG4-related disease[J]. JCI Insight, 2023, 8(17): e167602. DOI:10.1172/jci.insight.167602.
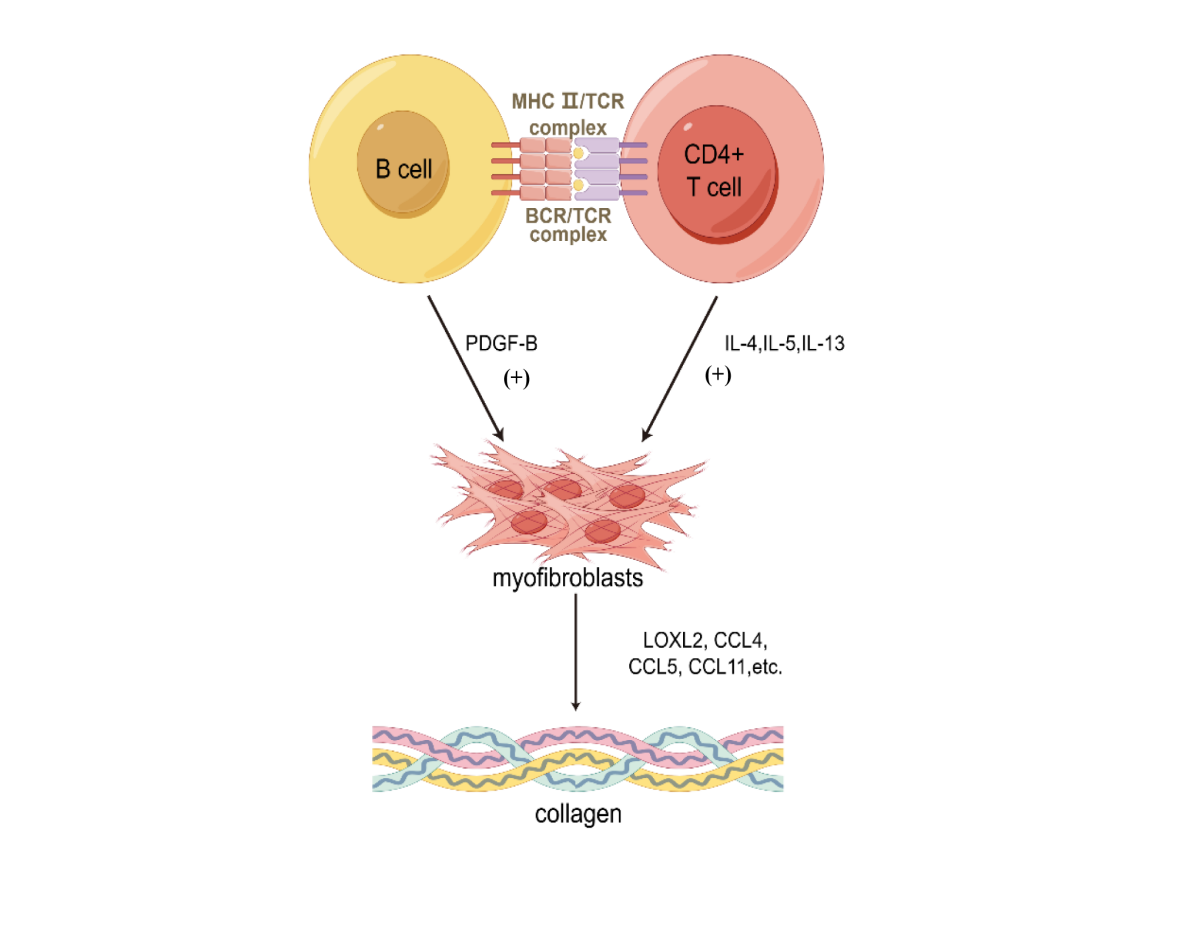
10、Della-Torre E, Rigamonti E, Perugino C, et al. B lymphocytes directly contribute to tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG(4)-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2020, 145(3): 968-981.e14. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.07.004.Della-Torre E, Rigamonti E, Perugino C, et al. B lymphocytes directly contribute to tissue fibrosis in patients with IgG(4)-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2020, 145(3): 968-981.e14. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.07.004.
11、Perugino CA, Kaneko N, Maehara T, et al. CD4+ and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes may induce mesenchymal cell apoptosis in IgG(4)-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2021, 147(1): 368-382. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.022.Perugino CA, Kaneko N, Maehara T, et al. CD4+ and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes may induce mesenchymal cell apoptosis in IgG(4)-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2021, 147(1): 368-382. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.022.
12、Heeringa JJ, Karim AF, van Laar JAM, et al. Expansion of blood IgG(4)(+) B, T(H)2, and regulatory T cells in patients with IgG(4)-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(5): 1831-1843.e10. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.07.024.Heeringa JJ, Karim AF, van Laar JAM, et al. Expansion of blood IgG(4)(+) B, T(H)2, and regulatory T cells in patients with IgG(4)-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(5): 1831-1843.e10. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.07.024.
13、Yang H, Wei R, Liu Q, et al. Frequency and distribution of CD4+CXCR5+ follicular B helper T cells within involved tissues in IgG4-related ophthalmic disease[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16(6): 9512-9520. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2017.7780. Yang H, Wei R, Liu Q, et al. Frequency and distribution of CD4+CXCR5+ follicular B helper T cells within involved tissues in IgG4-related ophthalmic disease[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 16(6): 9512-9520. DOI:10.3892/mmr.2017.7780.
14、Maehara T, Mattoo H, Ohta M, et al. Lesional CD4+ IFN-γ+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76(2): 377-385. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209139.Maehara T, Mattoo H, Ohta M, et al. Lesional CD4+ IFN-γ+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76(2): 377-385. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209139.
15、Kanari H, Kagami SI, Kashiwakuma D, et al. Role of Th2 cells in IgG4-related lacrimal gland enlargement[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2010, 152(Suppl 1): 47-53. DOI:10.1159/000312125.Kanari H, Kagami SI, Kashiwakuma D, et al. Role of Th2 cells in IgG4-related lacrimal gland enlargement[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2010, 152(Suppl 1): 47-53. DOI:10.1159/000312125.
16、Tsuboi H, Matsuo N, Iizuka M, et al. Analysis of IgG4 class switch-related molecules in IgG4-related disease[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2012, 14(4): R171. DOI:10.1186/ar3924.Tsuboi H, Matsuo N, Iizuka M, et al. Analysis of IgG4 class switch-related molecules in IgG4-related disease[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2012, 14(4): R171. DOI:10.1186/ar3924.
17、Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Maehara T, et al. Clonal expansion of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2016, 138(3): 825-838. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.12.1330.Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Maehara T, et al. Clonal expansion of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in patients with IgG4-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2016, 138(3): 825-838. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.12.1330.
18、Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Della-Torre E, et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2014, 134(3): 679-687. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.034.Mattoo H, Mahajan VS, Della-Torre E, et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2014, 134(3): 679-687. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.03.034.
19、Munemura R, Maehara T, Murakami Y, et al. Distinct disease-specific Tfh cell populations in 2 different fibrotic diseases: IgG(4)-related disease and Kimura disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2022, 150(2): 440-455.e17. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.03.034.Munemura R, Maehara T, Murakami Y, et al. Distinct disease-specific Tfh cell populations in 2 different fibrotic diseases: IgG(4)-related disease and Kimura disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2022, 150(2): 440-455.e17. DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.03.034.
20、Hart PH, Vitti GF, Burgess DR, et al. Potential antiinflammatory effects of interleukin 4: suppression of human monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and prostaglandin E2[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1989, 86(10): 3803-3807. DOI:10.1073/pnas.86.10.3803.Hart PH, Vitti GF, Burgess DR, et al. Potential antiinflammatory effects of interleukin 4: suppression of human monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and prostaglandin E2[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1989, 86(10): 3803-3807. DOI:10.1073/pnas.86.10.3803.
21、Roeb E. Interleukin-13 (IL-13)-a pleiotropic cytokine involved in wound healing and fibrosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(16): 12884. DOI:10.3390/ijms241612884.Roeb E. Interleukin-13 (IL-13)-a pleiotropic cytokine involved in wound healing and fibrosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(16): 12884. DOI:10.3390/ijms241612884.
22、Lumsden RV, Worrell JC, Boylan D, et al. Modulation of pulmonary fibrosis by IL-13Rα2[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2015, 308(7): L710-L718. DOI:10.1152/ajplung.00120.2014.Lumsden RV, Worrell JC, Boylan D, et al. Modulation of pulmonary fibrosis by IL-13Rα2[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2015, 308(7): L710-L718. DOI:10.1152/ajplung.00120.2014.
23、Gieseck RL 3rd, Wilson MS, Wynn TA. Type 2 immunity in tissue repair and fibrosis[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18(1): 62-76. DOI:10.1038/nri.2017.90.Gieseck RL 3rd, Wilson MS, Wynn TA. Type 2 immunity in tissue repair and fibrosis[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2018, 18(1): 62-76. DOI:10.1038/nri.2017.90.
24、Zhang WJ, Chen SJ, Zhou SC, et al. Inflammasomes and fibrosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 643149. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2021.643149.Zhang WJ, Chen SJ, Zhou SC, et al. Inflammasomes and fibrosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 643149. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2021.643149.
25、Li L, Xiang T, Guo J, et al. Inhibition of ACSS2-mediated histone crotonylation alleviates kidney fibrosis via IL-1β-dependent macrophage activation and tubular cell senescence[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 3200. DOI:10.1038/s41467-024-47315-3.Li L, Xiang T, Guo J, et al. Inhibition of ACSS2-mediated histone crotonylation alleviates kidney fibrosis via IL-1β-dependent macrophage activation and tubular cell senescence[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 3200. DOI:10.1038/s41467-024-47315-3.
26、Abuharbeid S, Czubayko F, Aigner A. The fibroblast growth factor-binding protein FGF-BP[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2006, 38(9): 1463-1468. DOI:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.10.017.Abuharbeid S, Czubayko F, Aigner A. The fibroblast growth factor-binding protein FGF-BP[J]. Int J Biochem Cell Biol, 2006, 38(9): 1463-1468. DOI:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.10.017.
27、Liu X, Nurieva RI, Dong C. Transcriptional regulation of follicular T-helper (Tfh) cells[J]. Immunol Rev, 2013, 252(1): 139-145. DOI:10.1111/imr.12040. Liu X, Nurieva RI, Dong C. Transcriptional regulation of follicular T-helper (Tfh) cells[J]. Immunol Rev, 2013, 252(1): 139-145. DOI:10.1111/imr.12040.
28、Maehara T, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, et al. Interleukin-21 contributes to germinal centre formation and immunoglobulin G4 production in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz’s disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012, 71(12): 2011-2019. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201477.Maehara T, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, et al. Interleukin-21 contributes to germinal centre formation and immunoglobulin G4 production in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz’s disease[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2012, 71(12): 2011-2019. DOI:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201477.
29、Poholek AC, Hansen K, Hernandez SG, et al. In vivo regulation of Bcl6 and T follicular helper cell development[J]. J Immunol, 2010, 185(1): 313-326. DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.0904023.Poholek AC, Hansen K, Hernandez SG, et al. In vivo regulation of Bcl6 and T follicular helper cell development[J]. J Immunol, 2010, 185(1): 313-326. DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.0904023.
30、Beerli P, Palczewski M. Unified framework to evaluate panmixia and migration direction among multiple sampling locations[J]. Genetics, 2010, 185(1): 313-326. DOI:10.1534/genetics.109.112532.Beerli P, Palczewski M. Unified framework to evaluate panmixia and migration direction among multiple sampling locations[J]. Genetics, 2010, 185(1): 313-326. DOI:10.1534/genetics.109.112532.
31、Yamamoto M, Ohara M, Suzuki C, et al. Elevated IgG4 concentrations in serum of patients with Mikulicz’s disease[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2004, 33(6): 432-433. DOI:10.1080/03009740410006439.Yamamoto M, Ohara M, Suzuki C, et al. Elevated IgG4 concentrations in serum of patients with Mikulicz’s disease[J]. Scand J Rheumatol, 2004, 33(6): 432-433. DOI:10.1080/03009740410006439.
32、Takahira M, Kawano M, Zen Y, et al. IgG4-related chronic sclerosing dacryoadenitis[J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 2007, 125(11): 1575-1578. DOI:10.1001/archopht.125.11.1575.Takahira M, Kawano M, Zen Y, et al. IgG4-related chronic sclerosing dacryoadenitis[J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 2007, 125(11): 1575-1578. DOI:10.1001/archopht.125.11.1575.
33、McCarthy JM, White VA, Harris G, et al. Idiopathic sclerosing inflammation of the orbit: immunohistologic analysis and comparison with retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Mod Pathol, 1993, 6(5): 581-587.McCarthy JM, White VA, Harris G, et al. Idiopathic sclerosing inflammation of the orbit: immunohistologic analysis and comparison with retroperitoneal fibrosis[J]. Mod Pathol, 1993, 6(5): 581-587.
34、Hu Z, Chai J. Structural mechanisms in NLR inflammasome assembly and signaling[M]//Inflammasome Signaling and Bacterial Infections. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 23-42. DOI:10.1007/978-3-319-41171-2_2.Hu Z, Chai J. Structural mechanisms in NLR inflammasome assembly and signaling[M]//Inflammasome Signaling and Bacterial Infections. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 23-42. DOI:10.1007/978-3-319-41171-2_2.
35、Lorenz G, Darisipudi MN, Anders HJ. Canonical and non-canonical effects of the NLRP3 inflammasome in kidney inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2014, 29(1): 41-48. DOI:10.1093/ndt/gft332.Lorenz G, Darisipudi MN, Anders HJ. Canonical and non-canonical effects of the NLRP3 inflammasome in kidney inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2014, 29(1): 41-48. DOI:10.1093/ndt/gft332.
36、DeSantis DA, Ko CW, Wang L, et al. Constitutive activation of the Nlrc4 inflammasome prevents hepatic fibrosis and promotes hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2015, 2015: 909827. DOI:10.1155/2015/909827.DeSantis DA, Ko CW, Wang L, et al. Constitutive activation of the Nlrc4 inflammasome prevents hepatic fibrosis and promotes hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2015, 2015: 909827. DOI:10.1155/2015/909827.
37、Andrew N, Kearney D, Selva D. IgG4-related orbital disease: a meta-analysis and review[J]. Acta Ophthalmol, 2013, 91(8): 694-700. DOI:10.1111/j.1755-3768.2012.02526.x.Andrew N, Kearney D, Selva D. IgG4-related orbital disease: a meta-analysis and review[J]. Acta Ophthalmol, 2013, 91(8): 694-700. DOI:10.1111/j.1755-3768.2012.02526.x.
38、Fertin C, Nicolas JF, Gillery P, et al. Interleukin-4 stimulates collagen synthesis by normal and scleroderma fibroblasts in dermal equivalents[J]. Cell Mol Biol, 1991, 37(8): 823-829. Fertin C, Nicolas JF, Gillery P, et al. Interleukin-4 stimulates collagen synthesis by normal and scleroderma fibroblasts in dermal equivalents[J]. Cell Mol Biol, 1991, 37(8): 823-829.
39、Izbicki G, Or R, Christensen TG, et al. Bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in IL-4-overexpressing and knockout mice[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2002, 283(5): L1110-L1116. DOI:10.1152/ajplung.00107.2002.Izbicki G, Or R, Christensen TG, et al. Bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in IL-4-overexpressing and knockout mice[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2002, 283(5): L1110-L1116. DOI:10.1152/ajplung.00107.2002.
40、Liang H, Zhang Z, Yan J, et al. The IL-4 receptor α has a critical role in bone marrow-derived fibroblast activation and renal fibrosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2017, 92(6): 1433-1443. DOI:10.1016/j.kint.2017.04.021.Liang H, Zhang Z, Yan J, et al. The IL-4 receptor α has a critical role in bone marrow-derived fibroblast activation and renal fibrosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2017, 92(6): 1433-1443. DOI:10.1016/j.kint.2017.04.021.
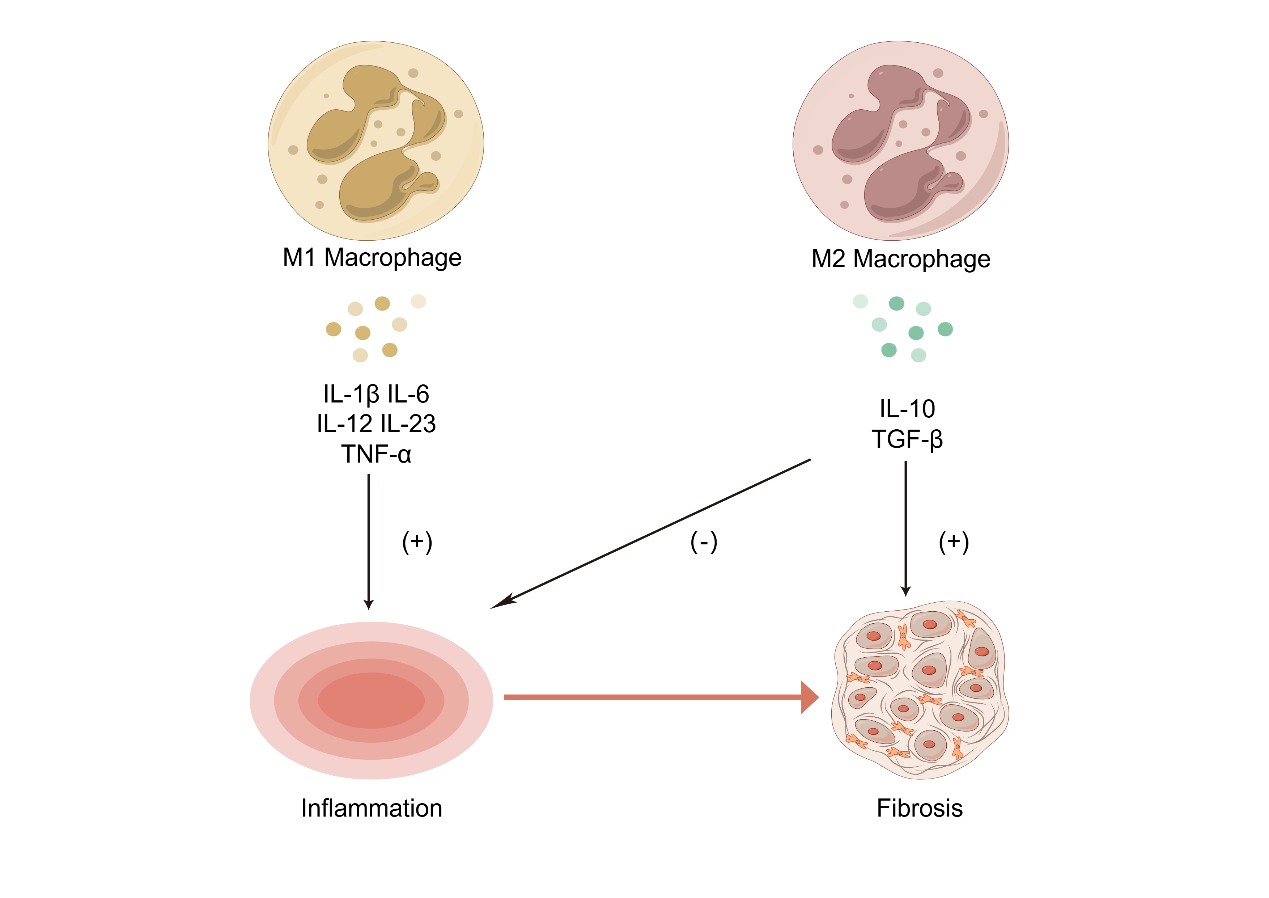
41、Mack M. Inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Matrix Biol, 2018, 68: 106-121. DOI:10.1016/j.matbio.2017.11.010.Mack M. Inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Matrix Biol, 2018, 68: 106-121. DOI:10.1016/j.matbio.2017.11.010.
42、Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-6440. DOI:10.1002/jcp.26429.Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(9): 6425-6440. DOI:10.1002/jcp.26429.
43、Weiskirchen R, Weiskirchen S, Tacke F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019, 65: 2-15. DOI:10.1016/j.mam.2018.06.003. Weiskirchen R, Weiskirchen S, Tacke F. Organ and tissue fibrosis: Molecular signals, cellular mechanisms and translational implications[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019, 65: 2-15. DOI:10.1016/j.mam.2018.06.003.