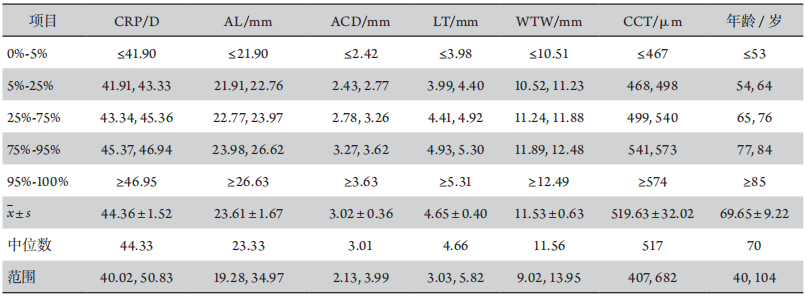
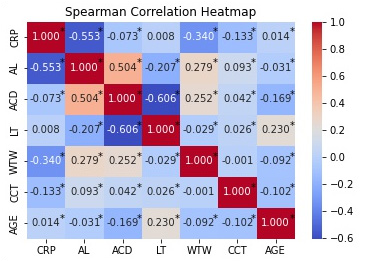
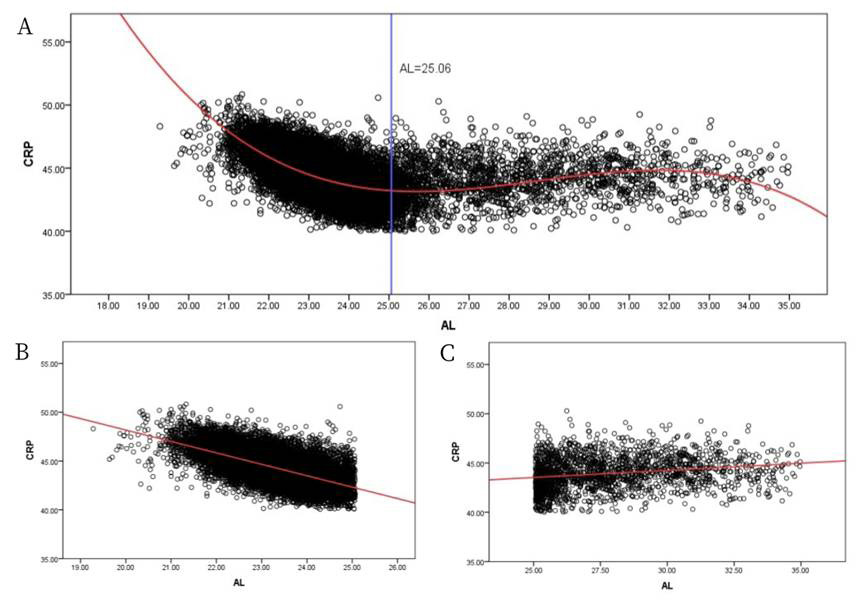
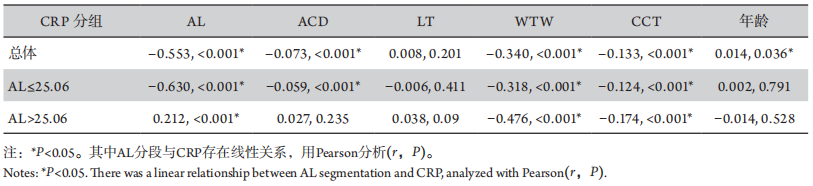
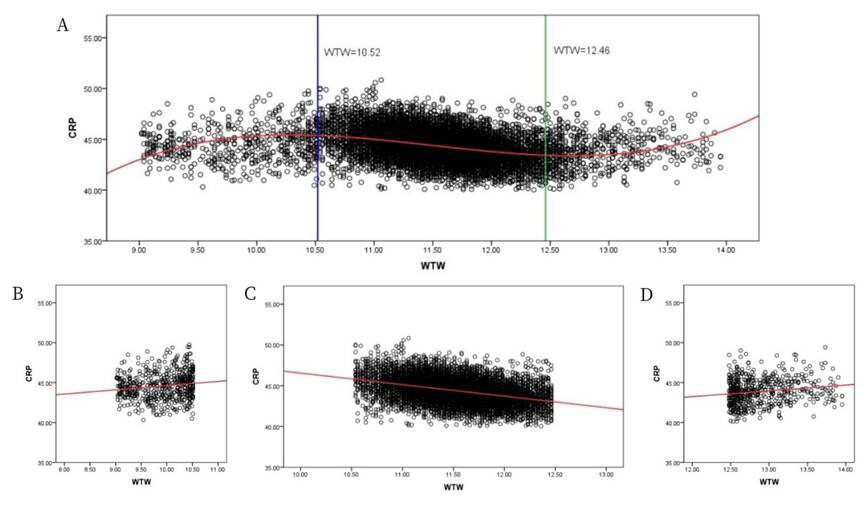
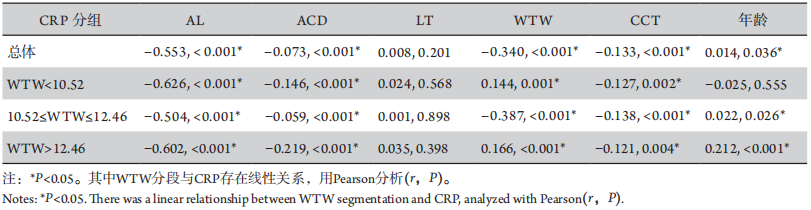
1、Olsen T. Calculation of intraocular lens power: a review[ J]. Acta
Ophthalmol Scand, 2007, 85(5): 472-485.Olsen T. Calculation of intraocular lens power: a review[ J]. Acta
Ophthalmol Scand, 2007, 85(5): 472-485.
2、Zhang C, Dai G, Pazo EE, et al. Accuracy of intraocular lens calculation
formulas in cataract patients with steep corneal curvature[ J]. PLoS
One, 2020, 15(11): e0241630.Zhang C, Dai G, Pazo EE, et al. Accuracy of intraocular lens calculation
formulas in cataract patients with steep corneal curvature[ J]. PLoS
One, 2020, 15(11): e0241630.
3、李修远, 常平骏, 赵云娥. 人工晶状体屈光度计算公式中有效晶
状体位置的预测及其影响因素[ J]. 国际眼科纵览, 2021, 45(5):
409-414.
Li XY, Chang PJ, Zhao YE. Prediction of effective lens position and
its influencing factors in the calculation formula of intraocular lens
refractive index[ J]. Int Rev Ophthalmol, 2021, 45 (5): 409-414.李修远, 常平骏, 赵云娥. 人工晶状体屈光度计算公式中有效晶
状体位置的预测及其影响因素[ J]. 国际眼科纵览, 2021, 45(5):
409-414.
Li XY, Chang PJ, Zhao YE. Prediction of effective lens position and
its influencing factors in the calculation formula of intraocular lens
refractive index[ J]. Int Rev Ophthalmol, 2021, 45 (5): 409-414.
4、李雪婷, 陈碧超, 李黄恩, 等. 扫频光相干生物测量仪在高度近
视白内障眼生物测量中的应用[ J]. 中华实验眼科杂志, 2020,
38(2):128-133.
Li X, Chen BC, Li HE, et al. Application of the swept-source coherence
tomography biometer in measurement for cataractous eyes with high
myopia[ J]. Chin J Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, 38(2):128-133.李雪婷, 陈碧超, 李黄恩, 等. 扫频光相干生物测量仪在高度近
视白内障眼生物测量中的应用[ J]. 中华实验眼科杂志, 2020,
38(2):128-133.
Li X, Chen BC, Li HE, et al. Application of the swept-source coherence
tomography biometer in measurement for cataractous eyes with high
myopia[ J]. Chin J Exp Ophthalmol, 2020, 38(2):128-133.
5、杨文利. 屈光性白内障手术的手术前规划与进展[ J]. 中国眼耳
鼻喉科杂志, 2022, 22(5): 435-438.
Yang WL. Preoperative planning and progress of refractive cataract
surgery[ J]. Chin J Ophthalmol Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 22(5): 435-
438.杨文利. 屈光性白内障手术的手术前规划与进展[ J]. 中国眼耳
鼻喉科杂志, 2022, 22(5): 435-438.
Yang WL. Preoperative planning and progress of refractive cataract
surgery[ J]. Chin J Ophthalmol Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 22(5): 435-
438.
6、Liu H, Xu Z, Qian Z, et al. Comparison of Ocular Biometry Profiles
in Urban and Rural Cataract Candidates in Eastern China[ J]. J
Ophthalmol, 2020,2020:2863698.Liu H, Xu Z, Qian Z, et al. Comparison of Ocular Biometry Profiles
in Urban and Rural Cataract Candidates in Eastern China[ J]. J
Ophthalmol, 2020,2020:2863698.
7、Yu JG, Zhong J, Mei ZM, et al. Evaluation of biometry and corneal
astigmatism in cataract surgery patients from Central China[ J]. BMC
Ophthalmol, 2017, 17(1): 56.Yu JG, Zhong J, Mei ZM, et al. Evaluation of biometry and corneal
astigmatism in cataract surgery patients from Central China[ J]. BMC
Ophthalmol, 2017, 17(1): 56.
8、Tomoyose E, Higa A, Sakai H, et al. Intraocular pressure and related
systemic and ocular biometric factors in a population-based study in
Japan: the Kumejima study[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2010, 150(2): 279-
286.Tomoyose E, Higa A, Sakai H, et al. Intraocular pressure and related
systemic and ocular biometric factors in a population-based study in
Japan: the Kumejima study[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2010, 150(2): 279-
286.
9、Natung T, Shullai W, Nongrum B, et al. Ocular biometry characteristics and corneal astigmatisms in cataract surgery candidates at a tertiary
care center in North-East India[ J]. Indian J Ophthalmol, 2019, 67(9):
1417-1423.Natung T, Shullai W, Nongrum B, et al. Ocular biometry characteristics and corneal astigmatisms in cataract surgery candidates at a tertiary
care center in North-East India[ J]. Indian J Ophthalmol, 2019, 67(9):
1417-1423.
10、Almorín-Fernández-Vigo I, Sánchez-Guillén I, Fernández-Vigo JI, et al.
Normative topographic anterior and posterior corneal astigmatism: axis
distribution and its relations with ocular and biometric parameters[ J].
J Clin Med, 2023, 12(11): 3664.Almorín-Fernández-Vigo I, Sánchez-Guillén I, Fernández-Vigo JI, et al.
Normative topographic anterior and posterior corneal astigmatism: axis
distribution and its relations with ocular and biometric parameters[ J].
J Clin Med, 2023, 12(11): 3664.
11、Hoffmann PC, Hütz W. Analysis of biometry and prevalence data for
corneal astigmatism in 23,239 eyes[ J]. J Cataract Refract Surg, 2010,
36(9): 1479-1485.Hoffmann PC, Hütz W. Analysis of biometry and prevalence data for
corneal astigmatism in 23,239 eyes[ J]. J Cataract Refract Surg, 2010,
36(9): 1479-1485.
12、Popov I, Waczulikova I, Stefanickova J, et al. Analysis of biometric
parameters of 2340 eyes measured with optical biometer Lenstar LS900
in a Caucasian population[ J]. Eur J Ophthalmol, 2022, 32(1): 213-220.Popov I, Waczulikova I, Stefanickova J, et al. Analysis of biometric
parameters of 2340 eyes measured with optical biometer Lenstar LS900
in a Caucasian population[ J]. Eur J Ophthalmol, 2022, 32(1): 213-220.
13、严梦南, 燕振国, 樊爱芳, 等. 青年近视人群屈光度与眼球生物学
参数的相关性[ J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2021, 21(4): 738-741.
Yan MN, Yan ZG, Fan AF, et al. Correlation of diopters and ocular
biometric parameters in youth with myopia[ J]. Int Eye Sci, 2021,
21(4): 738-741.严梦南, 燕振国, 樊爱芳, 等. 青年近视人群屈光度与眼球生物学
参数的相关性[ J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2021, 21(4): 738-741.
Yan MN, Yan ZG, Fan AF, et al. Correlation of diopters and ocular
biometric parameters in youth with myopia[ J]. Int Eye Sci, 2021,
21(4): 738-741.
14、Chen W, Zuo C, Chen C, et al. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism
before cataract surgery in Chinese patients[ J]. J Cataract Refract Surg,
2013, 39(2): 188-192.Chen W, Zuo C, Chen C, et al. Prevalence of corneal astigmatism
before cataract surgery in Chinese patients[ J]. J Cataract Refract Surg,
2013, 39(2): 188-192.
15、Fotedar R, Wang JJ, Burlutsky G, et al. Distribution of axial length and
ocular biometry measured using partial coherence laser interferometry
(IOL Master) in an older white population n[ J]. Ophthalmology,
2010,117(3): 417-423.Fotedar R, Wang JJ, Burlutsky G, et al. Distribution of axial length and
ocular biometry measured using partial coherence laser interferometry
(IOL Master) in an older white population n[ J]. Ophthalmology,
2010,117(3): 417-423.
16、Lei Q, Tu H, Feng X, et al. Distribution of ocular biometric parameters
and optimal model of anterior chamber depth regression in 28, 709
adult cataract patients in China using swept-source optical biometry[ J].
BMC Ophthalmol, 2021, 21(1): 178.Lei Q, Tu H, Feng X, et al. Distribution of ocular biometric parameters
and optimal model of anterior chamber depth regression in 28, 709
adult cataract patients in China using swept-source optical biometry[ J].
BMC Ophthalmol, 2021, 21(1): 178.
17、Grosvenor%20T.%20Reduction%20in%20axial%20length%20with%20age%3A%20an%20emmetropizing%20%0Amechanism%20for%20the%20adult%20eye%3F%5B%20J%5D.%20Am%20J%20Optom%20Physiol%20Opt%2C%201987%2C%20%0A64(9)%3A%20657-663.Grosvenor%20T.%20Reduction%20in%20axial%20length%20with%20age%3A%20an%20emmetropizing%20%0Amechanism%20for%20the%20adult%20eye%3F%5B%20J%5D.%20Am%20J%20Optom%20Physiol%20Opt%2C%201987%2C%20%0A64(9)%3A%20657-663.
18、Lu Q, Du Y, Zhang Y, et al. A genome-wide association study for
susceptibility to axial length in highly myopic eyes[ J]. Phenomics,
2023, 3(3): 255-267.Lu Q, Du Y, Zhang Y, et al. A genome-wide association study for
susceptibility to axial length in highly myopic eyes[ J]. Phenomics,
2023, 3(3): 255-267.
19、Wei L, He W, Meng J, et al. Evaluation of the white-to-white distance in
39, 986 Chinese cataractous eyes[ J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2021,
62(1): 7.Wei L, He W, Meng J, et al. Evaluation of the white-to-white distance in
39, 986 Chinese cataractous eyes[ J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2021,
62(1): 7.
20、王丹, 王晓睿, 韦伟, 等. 近视患者Corvis ST角膜生物力学参数
与眼部其他生物测量参数的相关分析[ J]. 眼科新进展, 2021,
41(4): 354-358.
Wang D, Wang XR, Wei W, et al. Correlation analysis between corneal
biomechanical parameters and other ocular biometric parameters of
Corvis ST in myopia patients [ J.] New Adv Ophthalmol, 2021, 41 (4):
354-358.王丹, 王晓睿, 韦伟, 等. 近视患者Corvis ST角膜生物力学参数
与眼部其他生物测量参数的相关分析[ J]. 眼科新进展, 2021,
41(4): 354-358.
Wang D, Wang XR, Wei W, et al. Correlation analysis between corneal
biomechanical parameters and other ocular biometric parameters of
Corvis ST in myopia patients [ J.] New Adv Ophthalmol, 2021, 41 (4):
354-358.