1、Song SJ, Wong TY. Current concepts in diabetic retinopathy[ J].
Diabetes Metab J, 2014, 38(6): 416-425.Song SJ, Wong TY. Current concepts in diabetic retinopathy[ J].
Diabetes Metab J, 2014, 38(6): 416-425.
2、Zhu Y, Cai X, Liu Y, et al. Serum albumin, but not bilirubin, is
associated with diabetic chronic vascular complications in a Chinese
Type 2 diabetic population[ J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 12086.Zhu Y, Cai X, Liu Y, et al. Serum albumin, but not bilirubin, is
associated with diabetic chronic vascular complications in a Chinese
Type 2 diabetic population[ J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 12086.
3、Iwasaki T, Togashi Y, Terauchi Y. Significant association of serum
albumin with severity of retinopathy and neuropathy, in addition to that
of nephropathy, in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients[ J]. Endocr J, 2008,
55(2): 311-316.Iwasaki T, Togashi Y, Terauchi Y. Significant association of serum
albumin with severity of retinopathy and neuropathy, in addition to that
of nephropathy, in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients[ J]. Endocr J, 2008,
55(2): 311-316.
4、Ferrucci L, Fabbri E. Inflammageing: chronic inflammation in ageing,
cardiovascular disease, and frailty[ J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2018, 15(9):
505-522.Ferrucci L, Fabbri E. Inflammageing: chronic inflammation in ageing,
cardiovascular disease, and frailty[ J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2018, 15(9):
505-522.
5、Kern TS. Contributions of inflammatory processes to the development
of the early stages of diabetic retinopathy[ J]. Exp Diabetes Res, 2007,
2007: 95103.Kern TS. Contributions of inflammatory processes to the development
of the early stages of diabetic retinopathy[ J]. Exp Diabetes Res, 2007,
2007: 95103.
6、Jha JC, Ho F, Dan C, et al. A causal link between oxidative stress and
inflammation in cardiovascular and renal complications of diabetes[ J].
Clin Sci (Lond), 2018, 132(16): 1811-1836.Jha JC, Ho F, Dan C, et al. A causal link between oxidative stress and
inflammation in cardiovascular and renal complications of diabetes[ J].
Clin Sci (Lond), 2018, 132(16): 1811-1836.
7、Yaribeygi H, Atkin SL, Sahebkar A. A review of the molecular
mechanisms of hyperglycemia‐induced free radical generation leading
to oxidative stress[ J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(2): 1300-1312.Yaribeygi H, Atkin SL, Sahebkar A. A review of the molecular
mechanisms of hyperglycemia‐induced free radical generation leading
to oxidative stress[ J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(2): 1300-1312.
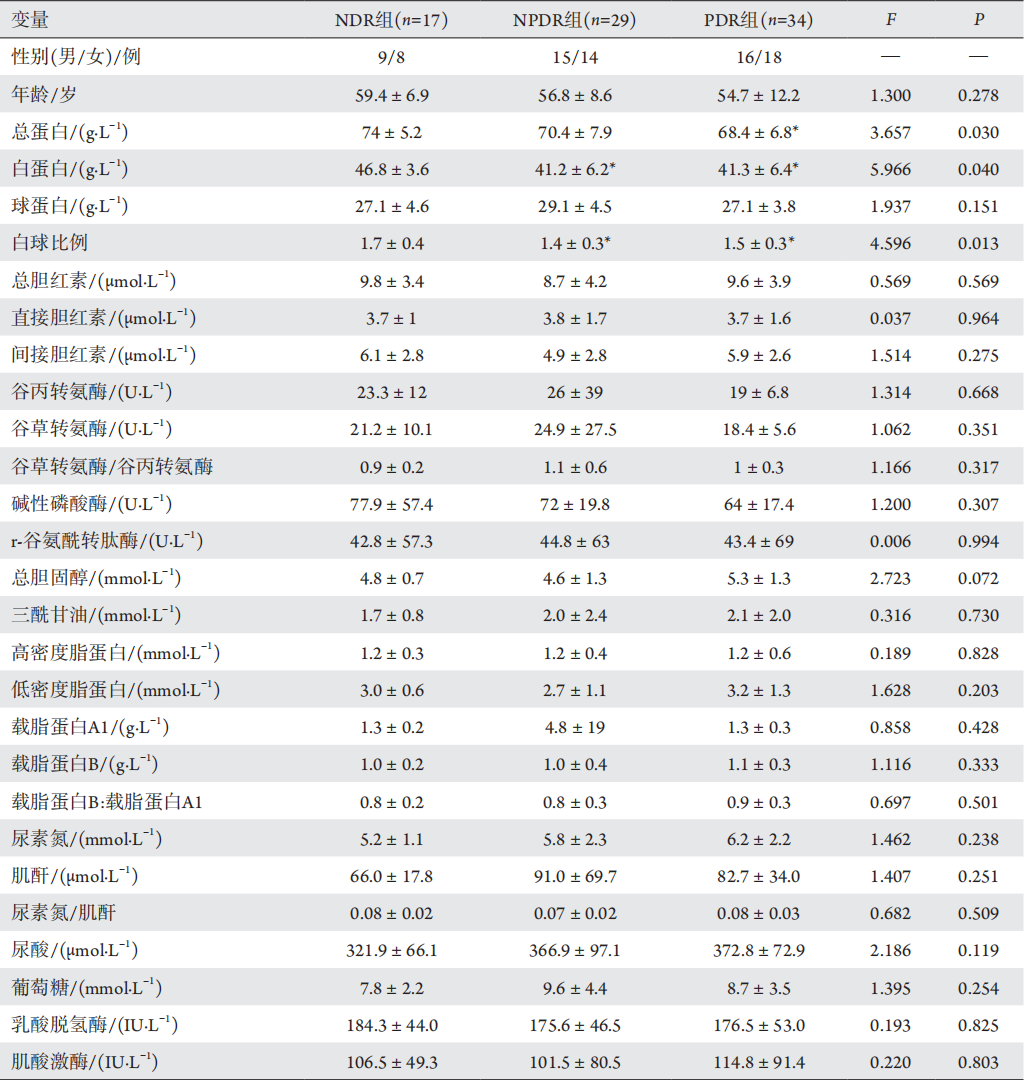
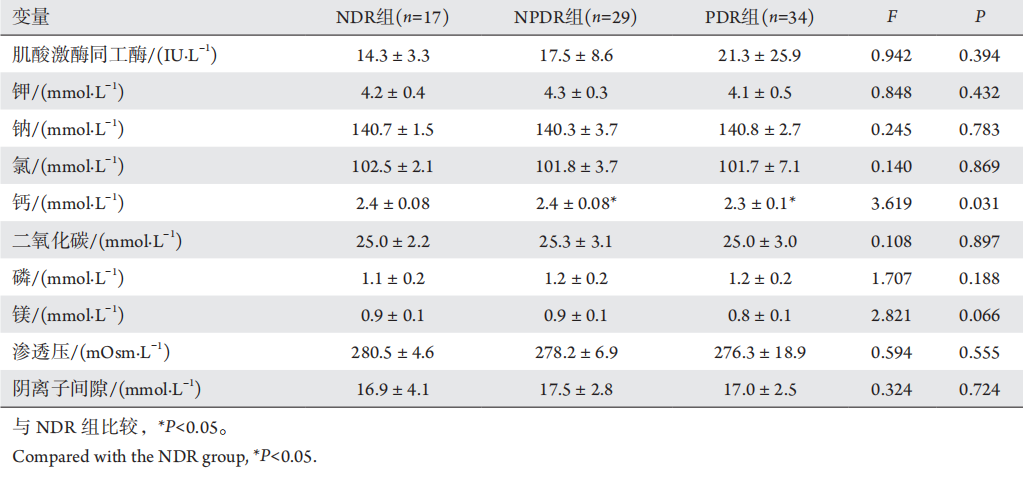
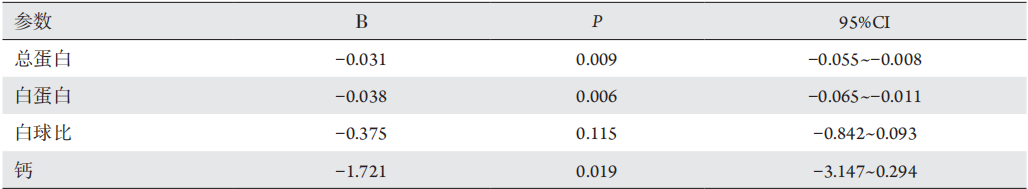
8、王珊珊, 陈莉明, 常宝成, 等. 2型糖尿病患者血清钙与糖代谢的
相关关系[ J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2014, 30(1): 26-30.
WANG SS, CHEN LiM, CHANG BC, et al. The
correlation between serum calcium and glucose metabolism in patients
with type 2 diabetes[ J]. Chinese Journal of Endocrinology and
Metabolism, 2014, 30(1): 26-30.王珊珊, 陈莉明, 常宝成, 等. 2型糖尿病患者血清钙与糖代谢的
相关关系[ J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2014, 30(1): 26-30.
WANG SS, CHEN LiM, CHANG BC, et al. The
correlation between serum calcium and glucose metabolism in patients
with type 2 diabetes[ J]. Chinese Journal of Endocrinology and
Metabolism, 2014, 30(1): 26-30.