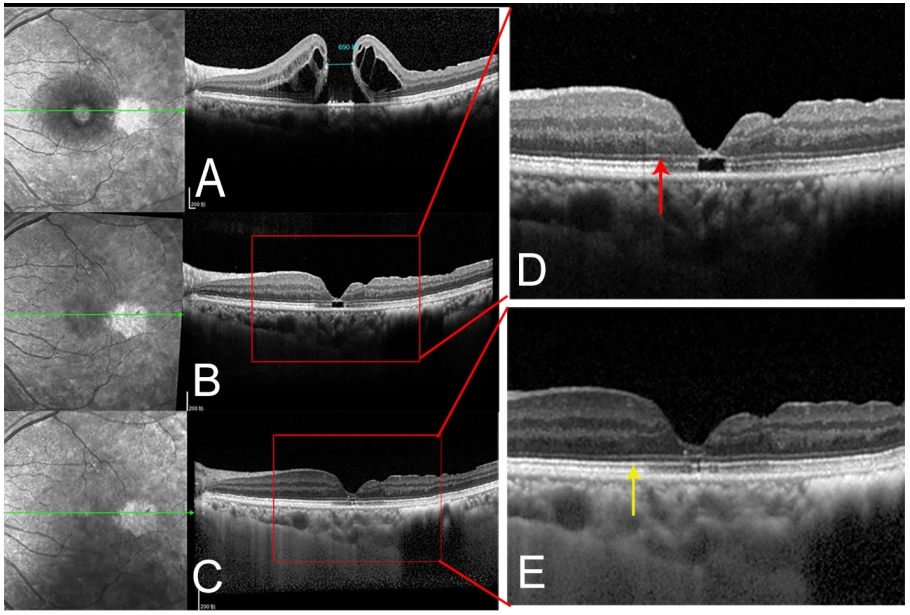
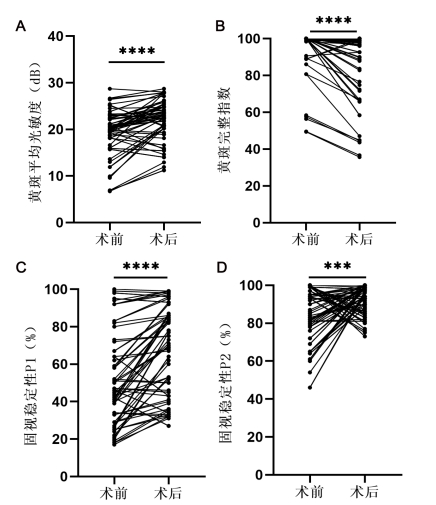
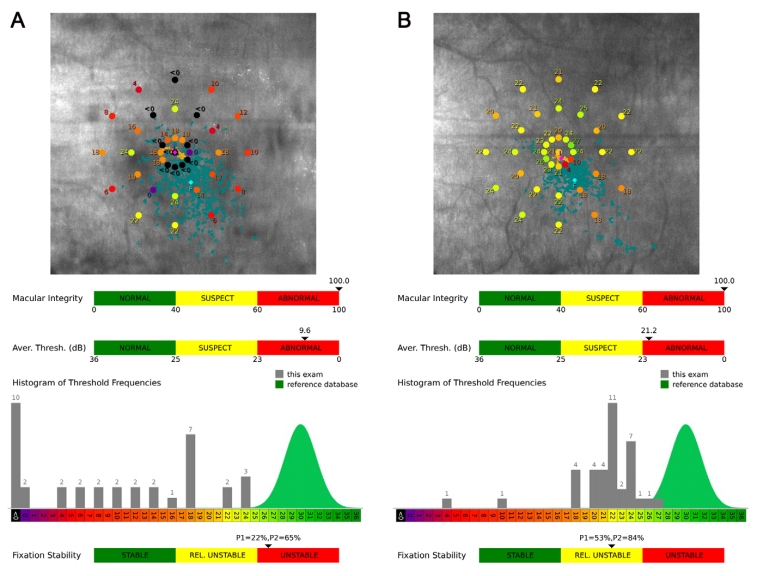
1、Gass JD. Idiopathic senile macular hole. Its early stages and
pathogenesis[ J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 1988, 106(5): 629-639. DOI: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060130683026.Gass JD. Idiopathic senile macular hole. Its early stages and
pathogenesis[ J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 1988, 106(5): 629-639. DOI: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060130683026.
2、Mester V, Kuhn F. Internal limiting membrane removal in the
management of full-thickness macular holes[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol,
2000, 129(6): 769-777. DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9394(00)00358-5.Mester V, Kuhn F. Internal limiting membrane removal in the
management of full-thickness macular holes[ J]. Am J Ophthalmol,
2000, 129(6): 769-777. DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9394(00)00358-5.
3、García-Arumí J, Martinez V, Puig J, et al. The role of vitreoretinal
surger y in the management of myopic macular hole without
retinal detachment[ J]. Retina, 2001, 21(4): 332-338. DOI:
10.1097/00006982-200108000-00006.García-Arumí J, Martinez V, Puig J, et al. The role of vitreoretinal
surger y in the management of myopic macular hole without
retinal detachment[ J]. Retina, 2001, 21(4): 332-338. DOI:
10.1097/00006982-200108000-00006.
4、Christensen UC. Value of internal limiting membrane peeling in surgery
for idiopathic macular hole and the correlation between function and
retinal morphology[ J]. Acta Ophthalmol, 2009, 87(thesis2): 1-23.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2009.01777.x.Christensen UC. Value of internal limiting membrane peeling in surgery
for idiopathic macular hole and the correlation between function and
retinal morphology[ J]. Acta Ophthalmol, 2009, 87(thesis2): 1-23.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2009.01777.x.
5、Michalewska Z, Michalewski J, Adelman RA, et al. Inverted internal
limiting membrane flap technique for large macular holes[ J].
Ophthalmology, 2010, 117(10): 2018-2025. DOI: 10.1016/
j.ophtha.2010.02.011.Michalewska Z, Michalewski J, Adelman RA, et al. Inverted internal
limiting membrane flap technique for large macular holes[ J].
Ophthalmology, 2010, 117(10): 2018-2025. DOI: 10.1016/
j.ophtha.2010.02.011.
6、Baumann C, Kaye S, Iannetta D, et al. Effect of inverted internal
limiting membrane flap on closure rate, postoperative visual acuity,
and restoration of outer retinal layers in primary idiopathic macular
hole surgery[ J]. Retina, 2020, 40(10): 1955-1963. DOI: 10.1097/
iae.0000000000002707.Baumann C, Kaye S, Iannetta D, et al. Effect of inverted internal
limiting membrane flap on closure rate, postoperative visual acuity,
and restoration of outer retinal layers in primary idiopathic macular
hole surgery[ J]. Retina, 2020, 40(10): 1955-1963. DOI: 10.1097/
iae.0000000000002707.
7、Mete M, Alfano A, Guerriero M, et al. Inverted internal limiting
membrane flap technique versus complete internal limiting
membrane removal in myopic macular hole surgery: a Comparative
Study[ J]. Retina, 2017, 37(10): 1923-1930. DOI: 10.1097/
IAE.0000000000001446.Mete M, Alfano A, Guerriero M, et al. Inverted internal limiting
membrane flap technique versus complete internal limiting
membrane removal in myopic macular hole surgery: a Comparative
Study[ J]. Retina, 2017, 37(10): 1923-1930. DOI: 10.1097/
IAE.0000000000001446.
8、Rizzo S, Tartaro R, Barca F, et al. Internal limiting membrane peeling
versus inverted flap technique for treatment of full-thickness macular
holes: a comparative study in a large series of patients[ J]. Retina, 2018,
38(Suppl 1): S73-S78. DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001985.Rizzo S, Tartaro R, Barca F, et al. Internal limiting membrane peeling
versus inverted flap technique for treatment of full-thickness macular
holes: a comparative study in a large series of patients[ J]. Retina, 2018,
38(Suppl 1): S73-S78. DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001985.
9、Shin MK, Park KH, Park SW, et al. Perfluoro-n-octane-assisted single�layered inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for macular
hole surgery[ J]. Retina, 2014, 34(9): 1905-1910. DOI: 10.1097/
IAE.0000000000000339.Shin MK, Park KH, Park SW, et al. Perfluoro-n-octane-assisted single�layered inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique for macular
hole surgery[ J]. Retina, 2014, 34(9): 1905-1910. DOI: 10.1097/
IAE.0000000000000339.
10、Han R, Zhang C, Zhao X, et al. Treatment of primary full-thickness
macular hole by intravitreal injection of expansile gas[ J]. Eye (Lond),
2019, 33(1): 136-143. DOI: 10.1038/s41433-018-0098-z.Han R, Zhang C, Zhao X, et al. Treatment of primary full-thickness
macular hole by intravitreal injection of expansile gas[ J]. Eye (Lond),
2019, 33(1): 136-143. DOI: 10.1038/s41433-018-0098-z.
11、Modi A, Giridhar A, Gopalakrishnan M. Sulfurhexafluoride (SF6)
versus perfluoropropane (c3f8) gas as tamponade in macular
hole surgery[ J]. Retina, 2017, 37(2): 283-290. DOI: 10.1097/
iae.0000000000001124.Modi A, Giridhar A, Gopalakrishnan M. Sulfurhexafluoride (SF6)
versus perfluoropropane (c3f8) gas as tamponade in macular
hole surgery[ J]. Retina, 2017, 37(2): 283-290. DOI: 10.1097/
iae.0000000000001124.
12、Mori K, Saito S, Gehlbach PL, et al. Treatment of stage 2 macular hole
by intravitreous injection of expansile gas and induction of posterior
vitreous detachment[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2007, 114(1): 127-133. DOI:
10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.07.001.Mori K, Saito S, Gehlbach PL, et al. Treatment of stage 2 macular hole
by intravitreous injection of expansile gas and induction of posterior
vitreous detachment[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2007, 114(1): 127-133. DOI:
10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.07.001.
13、Yu Y, Liang X, Wang Z, et al. Internal limiting membrane peeling and air
tamponade for stage iii and stage iv idiopathic macular hole[ J]. Retina,
2020, 40(1): 66-74. DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000002340.Yu Y, Liang X, Wang Z, et al. Internal limiting membrane peeling and air
tamponade for stage iii and stage iv idiopathic macular hole[ J]. Retina,
2020, 40(1): 66-74. DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000002340.
14、Chen X, Yao Y, Hao X, et al. A comparative study of vitrectomy
combined with internal limiting membrane peeling for the treatment of idiopathic macular hole with air or C3F8 intraocular tamponade[ J]. J
Ophthalmol, 2018, 2018: 1672501. DOI: 10.1155/2018/1672501.Chen X, Yao Y, Hao X, et al. A comparative study of vitrectomy
combined with internal limiting membrane peeling for the treatment of idiopathic macular hole with air or C3F8 intraocular tamponade[ J]. J
Ophthalmol, 2018, 2018: 1672501. DOI: 10.1155/2018/1672501.
15、Rohrschneider K, Bültmann S, Springer C. Use of fundus perimetry
(microperimetry) to quantify macular sensitivity[ J]. Prog Retin Eye
Res, 2008, 27(5): 536-548. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.07.003.Rohrschneider K, Bültmann S, Springer C. Use of fundus perimetry
(microperimetry) to quantify macular sensitivity[ J]. Prog Retin Eye
Res, 2008, 27(5): 536-548. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.07.003.
16、Midena E, Vujosevic S, Cavarzeran F, et al. Normal values for fundus
perimetry with the microperimeter MP1[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2010,
117(8): 1571-1576, 1576.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.12.044.Midena E, Vujosevic S, Cavarzeran F, et al. Normal values for fundus
perimetry with the microperimeter MP1[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2010,
117(8): 1571-1576, 1576.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2009.12.044.
17、Bové álvarez M, Sabaté S, Gómez-Resa M, et al. Anatomical and visual
outcomes of inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique versus
internal limiting membrane peeling in myopic macular hole without
retinal detachment: a Preliminary Retrospective Study[ J]. Retina,
2020, 40(2): 233-240. DOI: 10.1097/iae.0000000000002368.Bové álvarez M, Sabaté S, Gómez-Resa M, et al. Anatomical and visual
outcomes of inverted internal limiting membrane flap technique versus
internal limiting membrane peeling in myopic macular hole without
retinal detachment: a Preliminary Retrospective Study[ J]. Retina,
2020, 40(2): 233-240. DOI: 10.1097/iae.0000000000002368.
18、Itoh Y, Inoue M, Rii T, et al. Correlation between length of foveal cone
outer segment tips line defect and visual acuity after macular hole
closure[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2012, 119(7): 1438-1446. DOI: 10.1016/
j.ophtha.2012.01.023.Itoh Y, Inoue M, Rii T, et al. Correlation between length of foveal cone
outer segment tips line defect and visual acuity after macular hole
closure[ J]. Ophthalmology, 2012, 119(7): 1438-1446. DOI: 10.1016/
j.ophtha.2012.01.023.
19、Faria%20MY%2C%20Proen%C3%A7a%20H%2C%20Ferreira%20NG%2C%20et%20al.%20Inverted%20internal%20limiting%20%0Amembrane%20flap%20techniques%20and%20outer%20retinal%20layer%20structures%5B%20J%5D.%20Retina%2C%20%0A2020%2C%2040(7)%3A%201299-1305.%20DOI%3A%2010.1097%2FIAE.0000000000002607.Faria%20MY%2C%20Proen%C3%A7a%20H%2C%20Ferreira%20NG%2C%20et%20al.%20Inverted%20internal%20limiting%20%0Amembrane%20flap%20techniques%20and%20outer%20retinal%20layer%20structures%5B%20J%5D.%20Retina%2C%20%0A2020%2C%2040(7)%3A%201299-1305.%20DOI%3A%2010.1097%2FIAE.0000000000002607.
20、Park JH, Lee SM, Park SW, et al. Comparative analysis of large macular
hole surgery using an internal limiting membrane insertion versus
inverted flap technique[ J]. Br J Ophthalmol, 2019, 103(2): 245-250.
DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-311770.Park JH, Lee SM, Park SW, et al. Comparative analysis of large macular
hole surgery using an internal limiting membrane insertion versus
inverted flap technique[ J]. Br J Ophthalmol, 2019, 103(2): 245-250.
DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2017-311770.
21、Zhang Q, Zhao X, Huang X, et al. METAVISION: a novel system
for quantifying Metamorphopsia in patients with myopic traction
maculopathy[ J]. Br J Ophthalmol, 2024, 108(12): 1723-1728. DOI:
10.1136/bjo-2023-324175.Zhang Q, Zhao X, Huang X, et al. METAVISION: a novel system
for quantifying Metamorphopsia in patients with myopic traction
maculopathy[ J]. Br J Ophthalmol, 2024, 108(12): 1723-1728. DOI:
10.1136/bjo-2023-324175.
22、Ali FS, Stein JD, Blachley TS, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for
developing idiopathic macular hole among a diverse group of patients
throughout the United States[ J]. JAMA Ophthalmol, 2017, 135(4):
299-305. DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2016.5870.Ali FS, Stein JD, Blachley TS, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for
developing idiopathic macular hole among a diverse group of patients
throughout the United States[ J]. JAMA Ophthalmol, 2017, 135(4):
299-305. DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2016.5870.
23、Mittra RA, Kim JE, Han DP, et al. Sustained postoperative face-down
positioning is unnecessary for successful macular hole surgery[ J]. Br J
Ophthalmol, 2009, 93(5): 664-666. DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2008.148544.Mittra RA, Kim JE, Han DP, et al. Sustained postoperative face-down
positioning is unnecessary for successful macular hole surgery[ J]. Br J
Ophthalmol, 2009, 93(5): 664-666. DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2008.148544.
24、贺峰, 郑霖,董方田. 特发性全层黄斑裂孔手术中消毒空气与
全氟丙烷填充效果的比较[ J]. 中华眼科杂志, 2017, 53(5): 327-331.
DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2017.05.003.
He F, Zheng L, Dong FT. Comparison of the effects of sterilized air and
perfluoropropane gas filling in the surgery for
idiopathic full-thickness macular hole[ J]. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi , 2017, 53(5): 327-331. DOI: 10.3760/cma.
j.issn.0412-4081.2017.05.003.He F, Zheng L, Dong FT. Comparison of the effects of sterilized air and
perfluoropropane gas filling in the surgery for
idiopathic full-thickness macular hole[ J]. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi , 2017, 53(5): 327-331. DOI: 10.3760/cma.
j.issn.0412-4081.2017.05.003.
25、Tarita-Nistor L, González EG, Mandelcorn MS, et al. Fixation stability,
fixation location, and visual acuity after successful macular hole
surgery[ J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2009, 50(1): 84-89. DOI:
10.1167/iovs.08-2342.Tarita-Nistor L, González EG, Mandelcorn MS, et al. Fixation stability,
fixation location, and visual acuity after successful macular hole
surgery[ J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2009, 50(1): 84-89. DOI:
10.1167/iovs.08-2342.