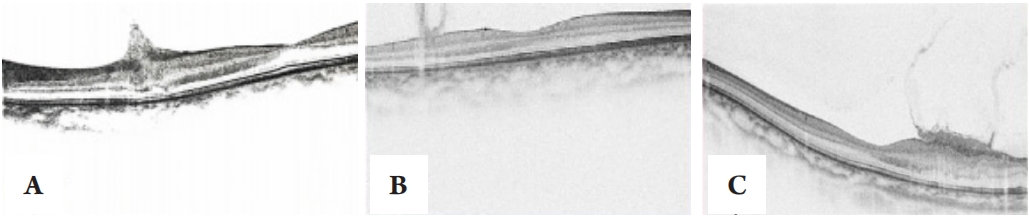
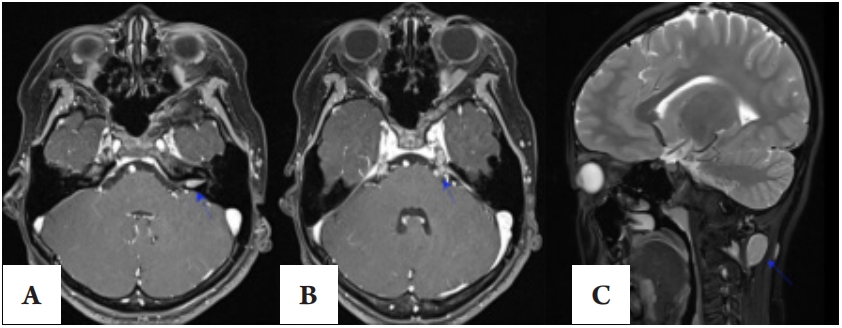
1、Kim BH, Chung YH, Woo TG, et al. NF2-related schwannomatosis
(NF2): molecular insights and therapeutic avenues[ J]. Int J Mol Sci,
2024, 25(12): 6558. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25126558.Kim BH, Chung YH, Woo TG, et al. NF2-related schwannomatosis
(NF2): molecular insights and therapeutic avenues[ J]. Int J Mol Sci,
2024, 25(12): 6558. DOI: 10.3390/ijms25126558.
2、Jiramongkolchai P, Schwartz MS, Friedman RA. Management of
neurofibromatosis type 2-associated vestibular schwannomas[ J].
Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2023, 56(3): 533-541. DOI: 10.1016/
j.otc.2023.02.012.Jiramongkolchai P, Schwartz MS, Friedman RA. Management of
neurofibromatosis type 2-associated vestibular schwannomas[ J].
Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2023, 56(3): 533-541. DOI: 10.1016/
j.otc.2023.02.012.
3、Wishart JH. Case of tumours in the skull, dura mater, and brain[ J].
Edinb Med Surg J, 1822,18(72): 393-397.Wishart JH. Case of tumours in the skull, dura mater, and brain[ J].
Edinb Med Surg J, 1822,18(72): 393-397.
4、Peyre M, Bernardeschi D, Sterkers O, et al. Natural history of vestibular
schwannomas and hearing loss in NF2 patients[ J]. Neurochirurgie,
2018, 64(5): 342-347. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2015.03.012.Peyre M, Bernardeschi D, Sterkers O, et al. Natural history of vestibular
schwannomas and hearing loss in NF2 patients[ J]. Neurochirurgie,
2018, 64(5): 342-347. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2015.03.012.
5、Baier M, Pitz S. Augenbeteiligung Bei neurofibromatose[ J]. Der
Ophthalmol, 2016, 113(5): 443-452. DOI: 10.1007/s00347-016-0237-5.Baier M, Pitz S. Augenbeteiligung Bei neurofibromatose[ J]. Der
Ophthalmol, 2016, 113(5): 443-452. DOI: 10.1007/s00347-016-0237-5.
6、Kunikata H, Nishiguchi KM, Watanabe M, et al. Surgical outcome
and pathological findings in macular epiretinal membrane caused by
neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Digit J Ophthalmol, 2022, 28(1): 12-16.
DOI: 10.5693/djo.02.2021.06.001.Kunikata H, Nishiguchi KM, Watanabe M, et al. Surgical outcome
and pathological findings in macular epiretinal membrane caused by
neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Digit J Ophthalmol, 2022, 28(1): 12-16.
DOI: 10.5693/djo.02.2021.06.001.
7、Waisberg V, Rodrigues LOC, Nehemy MB, et al. Spectral-domain
optical coherence tomography findings in neurofibromatosis type 2[ J].
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2016, 57(9): OCT262-OCT267. DOI:
10.1167/iovs.15-18919.Waisberg V, Rodrigues LOC, Nehemy MB, et al. Spectral-domain
optical coherence tomography findings in neurofibromatosis type 2[ J].
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2016, 57(9): OCT262-OCT267. DOI:
10.1167/iovs.15-18919.
8、Dinh CT, Nisenbaum E, Chyou D, et al. Genomics, epigenetics, and
hearing loss in neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Otol Neurotol, 2020,
41(5): e529-e537. DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002613.Dinh CT, Nisenbaum E, Chyou D, et al. Genomics, epigenetics, and
hearing loss in neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Otol Neurotol, 2020,
41(5): e529-e537. DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002613.
9、欧阳嘉敏, 高阳, 易珍, 等. 基于高通量测序分析鉴别视网膜病变
中的神经纤维瘤病[ J]. 眼科学报, 2024, 39(8): 381-394.
Ouyang JM, Gao Y, Yi Z, et al. Identification of neurofibromatosis in
retinopathy based on high-throughput sequencing analysis[ J]. Eye Sci,
2024, 39(8): 381-394.Ouyang JM, Gao Y, Yi Z, et al. Identification of neurofibromatosis in
retinopathy based on high-throughput sequencing analysis[ J]. Eye Sci,
2024, 39(8): 381-394.
10、Anand G, Vasallo G, Spanou M, et al. Diagnosis of sporadic
neurofibromatosis type 2 in the paediatric population[ J]. Arch Dis Child,
2018, 103(5): 463-469. DOI: 10.1136/archdischild- 2017-313154.Anand G, Vasallo G, Spanou M, et al. Diagnosis of sporadic
neurofibromatosis type 2 in the paediatric population[ J]. Arch Dis Child,
2018, 103(5): 463-469. DOI: 10.1136/archdischild- 2017-313154.
11、Filizoglu N, Ozguven S. Neurofibromatosis ty pe 2: multiple
meningiomatosis and vestibular schwannomas on 68 Ga-DOTATATE
PET/CT[ J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2022, 47(11): e710-e712. DOI: 10.1097/
RLU.0000000000004355.Filizoglu N, Ozguven S. Neurofibromatosis ty pe 2: multiple
meningiomatosis and vestibular schwannomas on 68 Ga-DOTATATE
PET/CT[ J]. Clin Nucl Med, 2022, 47(11): e710-e712. DOI: 10.1097/
RLU.0000000000004355.
12、王韵琪, 许传斌, 王昱昊. Ⅱ型神经纤维瘤病1例的影像特
征分析[ J]. 影像技术, 2024, 36(4): 54-58. DOI: 10.3969/
j.issn.1001-0270.2024.04.11.
Wang YQ, Xu CB, Wang YH. Imaging features analysis of 1 case of
type II neurofibromatosis[ J]. Image Technology, 2024, 36(4): 54-58.
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0270.2024.04.11.Wang YQ, Xu CB, Wang YH. Imaging features analysis of 1 case of
type II neurofibromatosis[ J]. Image Technology, 2024, 36(4): 54-58.
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0270.2024.04.11.
13、Coy S, Rashid R, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, et al. An update on the
CNS manifestations of neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Acta Neuropathol,
2020, 139(4): 643-665. DOI: 10.1007/s00401-019-02029-5.Coy S, Rashid R, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, et al. An update on the
CNS manifestations of neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Acta Neuropathol,
2020, 139(4): 643-665. DOI: 10.1007/s00401-019-02029-5.
14、Plotkin SR, Messiaen L, Legius E, et al. Updated diagnostic criteria and
nomenclature for neurofibromatosis type 2 and schwannomatosis: an
international consensus recommendation[ J]. Genet Med, 2022, 24(9):
1967-1977. DOI: 10.1016/j.gim.2022.05.007.Plotkin SR, Messiaen L, Legius E, et al. Updated diagnostic criteria and
nomenclature for neurofibromatosis type 2 and schwannomatosis: an
international consensus recommendation[ J]. Genet Med, 2022, 24(9):
1967-1977. DOI: 10.1016/j.gim.2022.05.007.
15、孙明霞, 徐冰, 李辉, 等. 神经纤维瘤病MR检查并文献分析[ J].
影像研究与医学应用, 2022, 6(4): 118-120,123.
Sun MX, Xu B, Li H, et al. MR examination of neurofibromatosis and
literature analysis[ J]. J Imag Res Med Appl, 2022, 6(4): 118-120+123.Sun MX, Xu B, Li H, et al. MR examination of neurofibromatosis and
literature analysis[ J]. J Imag Res Med Appl, 2022, 6(4): 118-120,123.
16、Zarei M, Hamzeloui P, Rooipoor R, et al. A case of neurofibromatosis
type 2 with unusual clinical features[ J]. Retin Cases Brief Rep, 2020,
14(1): 96-99. DOI: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000630.Zarei M, Hamzeloui P, Rooipoor R, et al. A case of neurofibromatosis
type 2 with unusual clinical features[ J]. Retin Cases Brief Rep, 2020,
14(1): 96-99. DOI: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000630.
17、Waisberg V, Rodrigues LOC, Nehemy MB, et al. Ocular alterations,
molecular findings, and three novel pathological mutations in a series
of NF2 patients[ J]. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2019, 257(7):
1453-1458. DOI: 10.1007/s00417-019-04348-5.Waisberg V, Rodrigues LOC, Nehemy MB, et al. Ocular alterations,
molecular findings, and three novel pathological mutations in a series
of NF2 patients[ J]. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 2019, 257(7):
1453-1458. DOI: 10.1007/s00417-019-04348-5.
18、Maria Bacci G, Giordano F, Sardi I, et al. Optical coherence
tomography significance in managing complex neurofibromatosis
2-related papilledema: Report of a case[ J]. JRSM Open, 2021, 12(1):
2054270420981454. DOI: 10.1177/2054270420981454.Maria Bacci G, Giordano F, Sardi I, et al. Optical coherence
tomography significance in managing complex neurofibromatosis
2-related papilledema: Report of a case[ J]. JRSM Open, 2021, 12(1):
2054270420981454. DOI: 10.1177/2054270420981454.
19、Ruggieri M, Praticò AD, Serra A, et al. Childhood neurofibromatosis
type 2 (NF2) and related disorders: from bench to bedside and
biologically targeted therapies[ J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2016,
36(5): 345-367. DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-1093.Ruggieri M, Praticò AD, Serra A, et al. Childhood neurofibromatosis
type 2 (NF2) and related disorders: from bench to bedside and
biologically targeted therapies[ J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2016,
36(5): 345-367. DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-1093.
20、Kang HM, Koh HJ, Chung EJ. Spectral-domain optical coherence
tomography of combined hamartoma of the retina and retinal pigment
epithelium in neurofibromatosis[ J]. Korean J Ophthalmol, 2013,
27(1): 68-71. DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2013.27.1.68.Kang HM, Koh HJ, Chung EJ. Spectral-domain optical coherence
tomography of combined hamartoma of the retina and retinal pigment
epithelium in neurofibromatosis[ J]. Korean J Ophthalmol, 2013,
27(1): 68-71. DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2013.27.1.68.
21、Emmanouil B, Wasik M, Charbel Issa P, et al. Structural abnormalities
of the central retina in neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Ophthalmic Res,
2022, 65(1): 77-85. DOI: 10.1159/000519143.Emmanouil B, Wasik M, Charbel Issa P, et al. Structural abnormalities
of the central retina in neurofibromatosis type 2[ J]. Ophthalmic Res,
2022, 65(1): 77-85. DOI: 10.1159/000519143.
22、Painter SL, Sipkova Z, Emmanouil B, et al. Neurofibromatosis
ty pe 2–related eye disease correlated w ith genetic severity
type[ J]. J Neuro Ophthalmol, 2019, 39(1): 44-49. DOI: 10.1097/
wno.0000000000000675.Painter SL, Sipkova Z, Emmanouil B, et al. Neurofibromatosis
ty pe 2–related eye disease correlated w ith genetic severity
type[ J]. J Neuro Ophthalmol, 2019, 39(1): 44-49. DOI: 10.1097/
wno.0000000000000675.
23、Moualed D, Wong J, Thomas O, et al. Prevalence and natural history
of schwannomas in neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): the influence of
pathogenic variants[ J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2022, 30(4): 458-464. DOI:
10.1038/s41431-021-01029-y.Moualed D, Wong J, Thomas O, et al. Prevalence and natural history
of schwannomas in neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2): the influence of
pathogenic variants[ J]. Eur J Hum Genet, 2022, 30(4): 458-464. DOI:
10.1038/s41431-021-01029-y.
24、Meyers SM, Gutman FA, Kaye LD, et al. Retinal changes associated
with neurofibromatosis 2[ J]. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc, 1995, 93:
245-252;discussion 252-257. DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70558-6.Meyers SM, Gutman FA, Kaye LD, et al. Retinal changes associated
with neurofibromatosis 2[ J]. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc, 1995, 93:
245-252;discussion 252-257. DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)70558-6.
25、Legoupil S, Bessis D, Picard F, et al. Dermatologic manifestations
in paediatric neurofibromatosis type 2: a cross sectional descriptive
multicentric study[ J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2022, 17(1): 242. DOI:
10.1186/s13023-022-02379-6.Legoupil S, Bessis D, Picard F, et al. Dermatologic manifestations
in paediatric neurofibromatosis type 2: a cross sectional descriptive
multicentric study[ J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2022, 17(1): 242. DOI:
10.1186/s13023-022-02379-6.