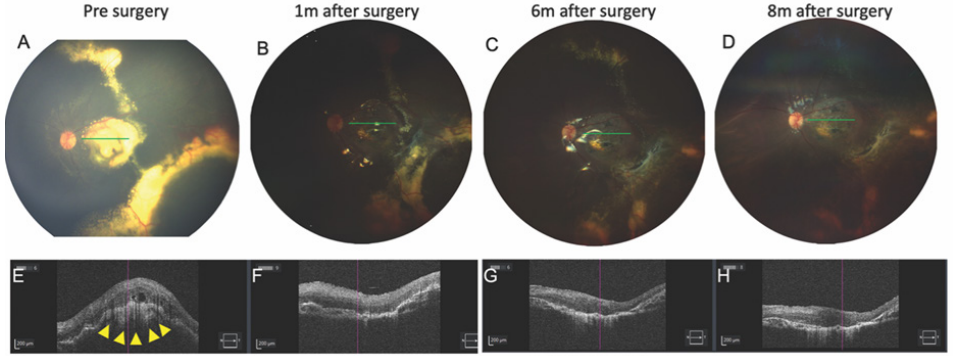
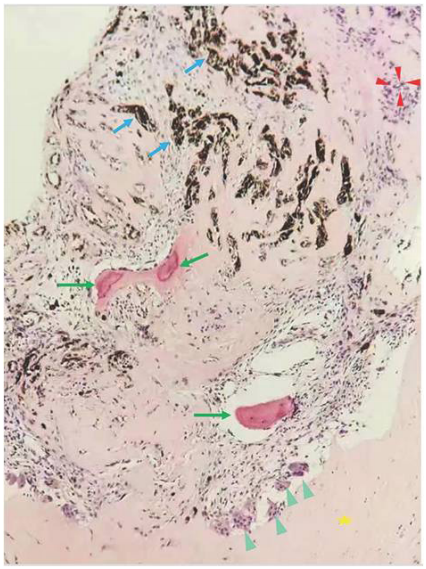
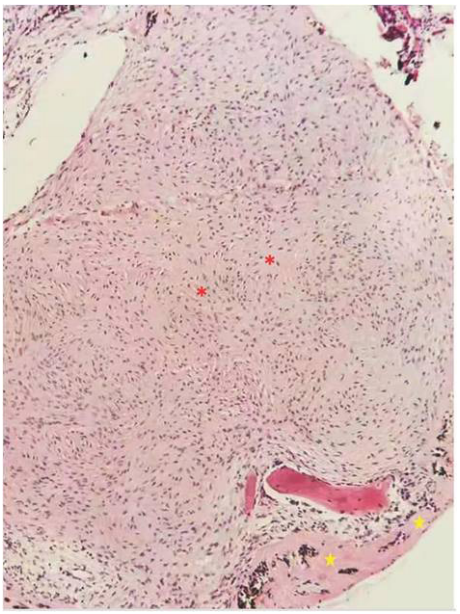
1、C.G(Coats G).Forms of retinal disease with massive
exudation. Royal London Ophthalmic Hospital Rep.
1908,17(3):440-525.C.G(Coats G).Forms of retinal disease with massive
exudation. Royal London Ophthalmic Hospital Rep.
1908,17(3):440-525.
2、Shields JA, Shields CL, Honavar SG, et al. Classification
and management of Coats disease: the 2000 Proctor
Lecture. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001, 131(5): 572-583. DOI:
10.1016/s0002-9394(01)00896-0.Shields JA, Shields CL, Honavar SG, et al. Classification
and management of Coats disease: the 2000 Proctor
Lecture. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001, 131(5): 572-583. DOI:
10.1016/s0002-9394(01)00896-0.
3、Altamirano F, Gonzalez E, Shah AS, et al. Preventable
vision loss in children with Coats disease. J AAPOS. 2024,
28(5): 104000. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2024.104000.Altamirano F, Gonzalez E, Shah AS, et al. Preventable
vision loss in children with Coats disease. J AAPOS. 2024,
28(5): 104000. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaapos.2024.104000.
4、Kang HG, Kim JD, Choi EY, et al. Clinical features and
prognostic factors in 71 eyes over 20years from patients
with Coats' disease in Korea. Sci Rep. 2021, 11(1): 6124.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85739-9.Kang HG, Kim JD, Choi EY, et al. Clinical features and
prognostic factors in 71 eyes over 20years from patients
with Coats' disease in Korea. Sci Rep. 2021, 11(1): 6124.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-85739-9.
5、Daruich AL, Moulin AP, Tran HV, et al. SUBFOVEAL
NODULE IN COATS' DISEASE: toward an updated
classification predicting visual prognosis. Retina. 2017,
37(8): 1591-1598. DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001399.Daruich AL, Moulin AP, Tran HV, et al. SUBFOVEAL
NODULE IN COATS' DISEASE: toward an updated
classification predicting visual prognosis. Retina. 2017,
37(8): 1591-1598. DOI: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001399.
6、Sigler EJ, Randolph JC, Calzada JI, et al. Current
management of Coats disease. Surv Ophthalmol. 2014,
59(1): 30-46. DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2013.03.007.Sigler EJ, Randolph JC, Calzada JI, et al. Current
management of Coats disease. Surv Ophthalmol. 2014,
59(1): 30-46. DOI: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2013.03.007.
7、Yiu G, Hang A, Fong R. Surgical drainage of large macular
cystoid spaces in Coats disease. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2024,
8(3): 355-358. DOI: 10.1177/24741264241240320.Yiu G, Hang A, Fong R. Surgical drainage of large macular
cystoid spaces in Coats disease. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2024,
8(3): 355-358. DOI: 10.1177/24741264241240320.
8、Sivalingam MD, Wakabayashi T, Kusaka S, et al. Lens�sparing perfluoro-octane-assisted external drainage of total
exudative retinal detachment in Coats' disease. Ophthalmic
Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2024, 55(8): 430-432. DOI: 10.3928/23258160-20240704-01.Sivalingam MD, Wakabayashi T, Kusaka S, et al. Lens�sparing perfluoro-octane-assisted external drainage of total
exudative retinal detachment in Coats' disease. Ophthalmic
Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2024, 55(8): 430-432. DOI: 10.3928/23258160-20240704-01.
9、Sears J, Capone A Jr, Sr TA, et al. Surgical management of
subfoveal neovascularization in children. Ophthalmology.
1999, 106(5): 920-924. DOI: 10.1016/S0161-
6420(99)00510-2.Sears J, Capone A Jr, Sr TA, et al. Surgical management of
subfoveal neovascularization in children. Ophthalmology.
1999, 106(5): 920-924. DOI: 10.1016/S0161-
6420(99)00510-2.
10、Melberg NS, Thomas MA, Burgess DB. The surgical
removal of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization.
Ingrowth site as a predictor of visual outcome. Retina.
1996, 16(3): 190-195. DOI: 10.1097/00006982-
199616030-00002.Melberg NS, Thomas MA, Burgess DB. The surgical
removal of subfoveal choroidal neovascularization.
Ingrowth site as a predictor of visual outcome. Retina.
1996, 16(3): 190-195. DOI: 10.1097/00006982-
199616030-00002.
11、Chang MM, McLean IW, Merritt JC. Coats' disease:
a study of 62 histologically confirmed cases. J Pediatr
Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984, 21(5): 163-168. DOI:
10.3928/0191-3913-19840901-03.Chang MM, McLean IW, Merritt JC. Coats' disease:
a study of 62 histologically confirmed cases. J Pediatr
Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984, 21(5): 163-168. DOI:
10.3928/0191-3913-19840901-03.
12、Hinz B. Myofibroblasts. Exp Eye Res. 2016,142:56-70.
DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.07.009.Hinz B. Myofibroblasts. Exp Eye Res. 2016,142:56-70.
DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.07.009.
13、Little K, Ma JH, Yang N, et al. Myofibroblasts in macular
fibrosis secondary to neovascular age-related macular
degeneration - the potential sources and molecular cues for
their recruitment and activation. EBioMedicine. 2018, 38:
283-291. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.029.Little K, Ma JH, Yang N, et al. Myofibroblasts in macular
fibrosis secondary to neovascular age-related macular
degeneration - the potential sources and molecular cues for
their recruitment and activation. EBioMedicine. 2018, 38:
283-291. DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.11.029.