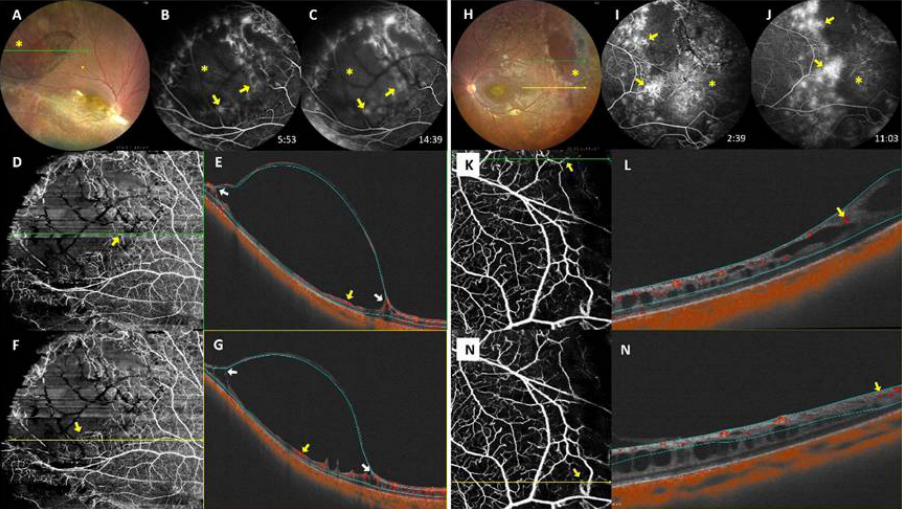
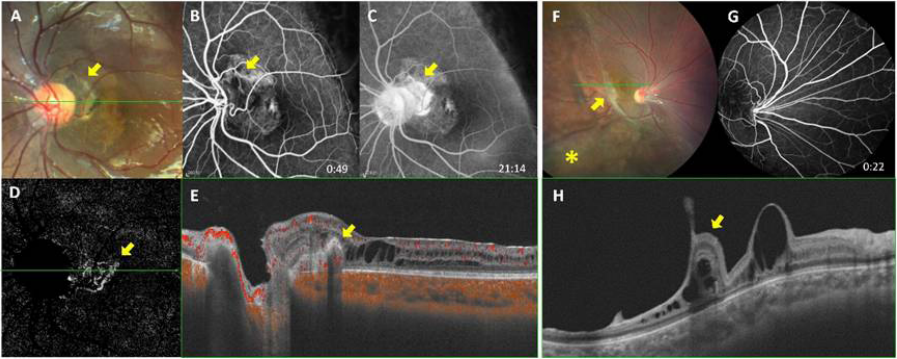
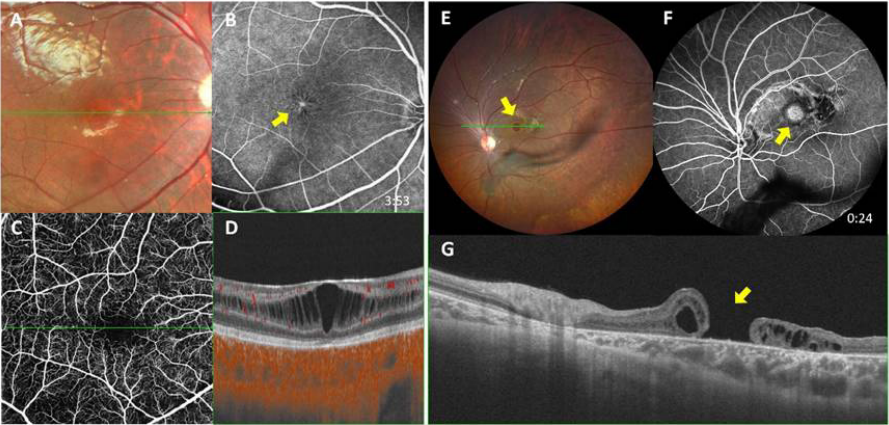
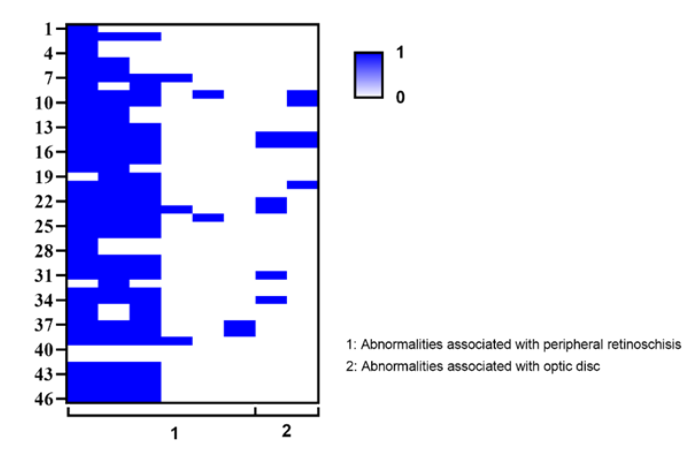
1、George ND, Yates JR, Moore AT. X linked retinoschisis.
Br J Ophthalmol. 1995,79(7):697-702. DOI:10.1136/
bjo.79.7.697.George ND, Yates JR, Moore AT. X linked retinoschisis.
Br J Ophthalmol. 1995,79(7):697-702. DOI:10.1136/
bjo.79.7.697.
2、Vijayasarathy C, Sardar Pasha SPB, Sieving PA. Of men
and mice: human X-linked retinoschisis and fidelity
in mouse modeling[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2022, 87:
100999. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100999.Vijayasarathy C, Sardar Pasha SPB, Sieving PA. Of men
and mice: human X-linked retinoschisis and fidelity
in mouse modeling[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2022, 87:
100999. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.100999.
3、Molday RS, Kellner U, Weber BHF. X-linked juvenile
retinoschisis: clinical diagnosis, genetic analysis, and
molecular mechanisms[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2012,
31(3): 195-212. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.12.002.Molday RS, Kellner U, Weber BHF. X-linked juvenile
retinoschisis: clinical diagnosis, genetic analysis, and
molecular mechanisms[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2012,
31(3): 195-212. DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.12.002.
4、Wakabayashi T, Chang E, Nudleman E, et al. Typical
and atypical clinical presentations of X-Linked
retinoschisis: a case series and literature review[J].
Surv Ophthalmol, 2023, 68(3): 347-360. DOI: 10.1016/
j.survophthal.2023.01.008.Wakabayashi T, Chang E, Nudleman E, et al. Typical
and atypical clinical presentations of X-Linked
retinoschisis: a case series and literature review[J].
Surv Ophthalmol, 2023, 68(3): 347-360. DOI: 10.1016/
j.survophthal.2023.01.008.
5、Molday LL, Hicks D, Sauer CG, et al. Expression of
X-linked retinoschisis protein RS1 in photoreceptor and
bipolar cells[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2001, 42(3):
816-825.Molday LL, Hicks D, Sauer CG, et al. Expression of
X-linked retinoschisis protein RS1 in photoreceptor and
bipolar cells[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2001, 42(3):
816-825.
6、Weber BHF, Schrewe H, Molday LL, et al. Inactivation
of the murine X-linked juvenile retinoschisis gene,
Rs1h, suggests a role of retinoschisin in retinal cell layer
organization and synaptic structure[J]. PNAS, 2002, 99(9):
6222-6227. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.092528599.Weber BHF, Schrewe H, Molday LL, et al. Inactivation
of the murine X-linked juvenile retinoschisis gene,
Rs1h, suggests a role of retinoschisin in retinal cell layer
organization and synaptic structure[J]. PNAS, 2002, 99(9):
6222-6227. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.092528599.
7、Sikkink SK, Biswas S, Parry NRA, et al. X-linked
retinoschisis: an update[J]. J Med Genet, 2007, 44(4): 225-
232. DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2006.047340.Sikkink SK, Biswas S, Parry NRA, et al. X-linked
retinoschisis: an update[J]. J Med Genet, 2007, 44(4): 225-
232. DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2006.047340.
8、George ND, Yates JR, Bradshaw K, et al. Infantile
presentation of X linked retinoschisis[J]. Br J Ophthalmol,
1995, 79(7): 653-657. DOI: 10.1136/bjo.79.7.653.George ND, Yates JR, Bradshaw K, et al. Infantile
presentation of X linked retinoschisis[J]. Br J Ophthalmol,
1995, 79(7): 653-657. DOI: 10.1136/bjo.79.7.653.
9、Parra MM, Hartnett ME. Vitreous hemorrhage in X-linked
retinoschisis[J]. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep, 2022, 25:
101395. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101395.Parra MM, Hartnett ME. Vitreous hemorrhage in X-linked
retinoschisis[J]. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep, 2022, 25:
101395. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101395.
10、Lee Y, Oh BL. Retinal detachment in X-linked
retinoschisis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(12): 1149. DOI:
10.1056/NEJMicm1904890.Lee Y, Oh BL. Retinal detachment in X-linked
retinoschisis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(12): 1149. DOI:
10.1056/NEJMicm1904890.
11、Patel NA, Laura D, Tran KD, et al. Retinal vasproliferative
tumor in a case of X-linked retinoschisis detachment[J].
Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep, 2018, 9: 48-50. DOI:
10.1016/j.ajoc.2018.01.002.Patel NA, Laura D, Tran KD, et al. Retinal vasproliferative
tumor in a case of X-linked retinoschisis detachment[J].
Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep, 2018, 9: 48-50. DOI:
10.1016/j.ajoc.2018.01.002.
12、Fan KC, McAllister MA, Yannuzzi NA, et al. X-Linked
retinoschisis and a Coats-Like response in the setting
of retinopathy of prematurity. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2020,
4(6): 525-529. DOI: 10.1177/2474126420939734.Fan KC, McAllister MA, Yannuzzi NA, et al. X-Linked
retinoschisis and a Coats-Like response in the setting
of retinopathy of prematurity. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2020,
4(6): 525-529. DOI: 10.1177/2474126420939734.
13、Yu J, Ni Y, Keane PA, et al. Foveomacular schisis in
juvenile X-linked retinoschisis: an optical coherence
tomography study[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2010, 149(6):
973-978.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2010.01.031.Yu J, Ni Y, Keane PA, et al. Foveomacular schisis in
juvenile X-linked retinoschisis: an optical coherence
tomography study[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 2010, 149(6):
973-978.e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2010.01.031.
14、Tantri A, Vrabec TR, Cu-Unjieng A, et al. X-linked
retinoschisis: a clinical and molecular genetic review[J].
Surv Ophthalmol, 2004, 49(2): 214-230. DOI: 10.1016/
j.survophthal.2003.12.007.Tantri A, Vrabec TR, Cu-Unjieng A, et al. X-linked
retinoschisis: a clinical and molecular genetic review[J].
Surv Ophthalmol, 2004, 49(2): 214-230. DOI: 10.1016/
j.survophthal.2003.12.007.
15、Green JL Jr, Jampol LM. Vascular opacification and
leakage in X-linked (juvenile) retinoschisis[J]. Br J
Ophthalmol, 1979, 63(5): 368-373. DOI: 10.1136/
bjo.63.5.368.Green JL Jr, Jampol LM. Vascular opacification and
leakage in X-linked (juvenile) retinoschisis[J]. Br J
Ophthalmol, 1979, 63(5): 368-373. DOI: 10.1136/
bjo.63.5.368.
16、Fahim AT, Ali N, Blachley T, et al. Peripheral
fundus findings in X-linked retinoschisis[J]. Br J
Ophthalmol, 2017, 101(11): 1555-1559. DOI: 10.1136/
bjophthalmol-2016-310110.Fahim AT, Ali N, Blachley T, et al. Peripheral
fundus findings in X-linked retinoschisis[J]. Br J
Ophthalmol, 2017, 101(11): 1555-1559. DOI: 10.1136/
bjophthalmol-2016-310110.
17、George ND, Yates JR, Moore AT. Clinical features in
affected males with X-linked retinoschisis[J]. Arch
Ophthalmol, 1996, 114(3): 274-280. DOI: 10.1001/
archopht.1996.01100130270007.George ND, Yates JR, Moore AT. Clinical features in
affected males with X-linked retinoschisis[J]. Arch
Ophthalmol, 1996, 114(3): 274-280. DOI: 10.1001/
archopht.1996.01100130270007.
18、Rao P, Robinson J, Yonekawa Y, et al. Wide-field imaging
of nonexudative and exudative congenital X-linked
retinoschisis[J]. Retina, 2016, 36(6): 1093-1100. DOI:
10.1097/IAE.0000000000000897.Rao P, Robinson J, Yonekawa Y, et al. Wide-field imaging
of nonexudative and exudative congenital X-linked
retinoschisis[J]. Retina, 2016, 36(6): 1093-1100. DOI:
10.1097/IAE.0000000000000897.
19、Al-Khersan H, Sengillo J, Fan KC, et al. Widefield
fluorescein angiography findings in pediatric patients with
X-linked retinoschisis[J]. Ophthalmol Retina, 2023, 7(7):
639-643. DOI: 10.1016/j.oret.2023.02.005.Al-Khersan H, Sengillo J, Fan KC, et al. Widefield
fluorescein angiography findings in pediatric patients with
X-linked retinoschisis[J]. Ophthalmol Retina, 2023, 7(7):
639-643. DOI: 10.1016/j.oret.2023.02.005.
20、Faatz H, Rothaus K, Ziegler M, et al. Vascular analysis
of type 1, 2, and 3 macular neovascularization in age�related macular degeneration using swept-source optical
coherence tomography angiography shows new insights
into differences of pathologic vasculature and may lead
to a more personalized understanding[J]. Biomedicines,
2022, 10(3): 694. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030694.Faatz H, Rothaus K, Ziegler M, et al. Vascular analysis
of type 1, 2, and 3 macular neovascularization in age�related macular degeneration using swept-source optical
coherence tomography angiography shows new insights
into differences of pathologic vasculature and may lead
to a more personalized understanding[J]. Biomedicines,
2022, 10(3): 694. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030694.
21、Piquin G , Abdelmassih Y, Martin G , et al .
SYMPTOM ATICEARLY- ONSETX - LINKED
RETINOSCHISIS: Clinical Presentation and Outcomes.
Retina. 2023, 43(2): 348-355. DOI:10.1097/IAE.
0000000000003667Piquin G , Abdelmassih Y, Martin G , et al .
SYMPTOM ATICEARLY- ONSETX - LINKED
RETINOSCHISIS: Clinical Presentation and Outcomes.
Retina. 2023, 43(2): 348-355. DOI:10.1097/IAE.
0000000000003667
22、Brodsky MC. Congenital optic disk anomalies[J]. Surv
Ophthalmol, 1994, 39(2): 89-112. DOI: 10.1016/0039-
6257(94)90155-4.Brodsky MC. Congenital optic disk anomalies[J]. Surv
Ophthalmol, 1994, 39(2): 89-112. DOI: 10.1016/0039-
6257(94)90155-4.
23、Caccamise WC. Situs inversus of the optic disc with
inferior conus and variable myopia: a case report[J]. Am
J Ophthalmol, 1954, 38(6): 854-856. DOI: 10.1016/0002-
9394(54)90418-3.Caccamise WC. Situs inversus of the optic disc with
inferior conus and variable myopia: a case report[J]. Am
J Ophthalmol, 1954, 38(6): 854-856. DOI: 10.1016/0002-
9394(54)90418-3.
24、Cohen SY, Vignal-Clermont C, Trinh L, et al. Tilted disc
syndrome (TDS): new hypotheses for posterior segment
complications and their implications in other retinal
diseases[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2022, 88: 101020. DOI:
10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101020.Cohen SY, Vignal-Clermont C, Trinh L, et al. Tilted disc
syndrome (TDS): new hypotheses for posterior segment
complications and their implications in other retinal
diseases[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2022, 88: 101020. DOI:
10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101020.
25、Kang S, Jin S, Roh KH, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve
fiber layer and optic nerve head characteristics in eyes
with situs inversus of the optic disc[J]. J Glaucoma, 2015,
24(4): 306-310. DOI: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31829e1ba2.Kang S, Jin S, Roh KH, et al. Peripapillary retinal nerve
fiber layer and optic nerve head characteristics in eyes
with situs inversus of the optic disc[J]. J Glaucoma, 2015,
24(4): 306-310. DOI: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31829e1ba2.
26、Zhang L, Liu X, Sun L, et al. Choroidal neovascularisation
secondary toX-linked retinoschisis[J]. Br J Ophthalm
ol,2024,108(11):1564-1570. DOI: 10.1136/bjo-2023-
324165.Zhang L, Liu X, Sun L, et al. Choroidal neovascularisation
secondary toX-linked retinoschisis[J]. Br J Ophthalm
ol,2024,108(11):1564-1570. DOI: 10.1136/bjo-2023-
324165.