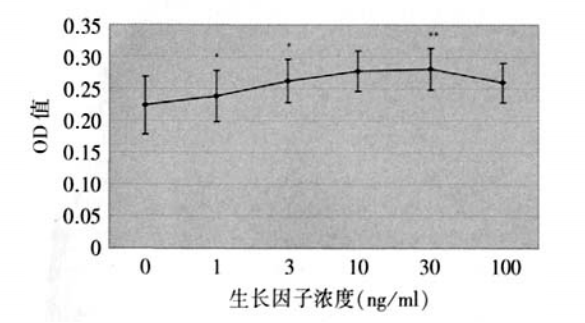
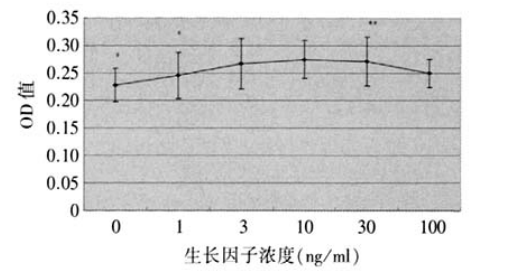
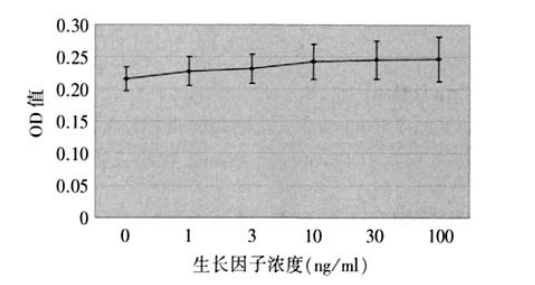
1、 Hollingsworth J.,Perez-Gomez I., Mutalib H.A., et al.A populalion study of the normal cornea using an in vivoslitscanning confocal microscope. Optom. Vis. Sci, 2001 ;78(10):706-711. Hollingsworth J.,Perez-Gomez I., Mutalib H.A., et al.A populalion study of the normal cornea using an in vivoslitscanning confocal microscope. Optom. Vis. Sci, 2001 ;78(10):706-711.
2、 Joyce NC , Hanis DL, Mello DM. Mechanisms of mitoticinhibition in coreal endothelium: contact inhibition andTGF-beta2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2002;43:2152-2159. Joyce NC , Hanis DL, Mello DM. Mechanisms of mitoticinhibition in coreal endothelium: contact inhibition andTGF-beta2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2002;43:2152-2159.
3、 Nagle A, Hur W, Gray NS. Antimitotic agents of naturalorigin.Curr Drug Targets,2006;7(3): 305-326. Nagle A, Hur W, Gray NS. Antimitotic agents of naturalorigin.Curr Drug Targets,2006;7(3): 305-326.
4、Wilson SE, lloyd SA, He YG, Extended life of humancorneal endothelial cells transfected with the SV40 largeT antigen.Invest.Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 1993;34(6):2112-2123.Wilson SE, lloyd SA, He YG, Extended life of humancorneal endothelial cells transfected with the SV40 largeT antigen.Invest.Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 1993;34(6):2112-2123.
5、Yu JY,DeRuiter SL, Tumer DL. RNA interference byexpression of short-interfering RNAs and hairpin RNAs inmammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2002; 99(9):6047-6052.Yu JY,DeRuiter SL, Tumer DL. RNA interference byexpression of short-interfering RNAs and hairpin RNAs inmammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2002; 99(9):6047-6052.
6、Namiki M, Tagami Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Presence ofhuman epidermal growth factor (hEGF), basic fibrblastgrowth factor (bFGF)in human aqueous. Nippon GankaGakkai Zasshi,1992;96(5):652-656.Namiki M, Tagami Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Presence ofhuman epidermal growth factor (hEGF), basic fibrblastgrowth factor (bFGF)in human aqueous. Nippon GankaGakkai Zasshi,1992;96(5):652-656.
7、Tripathi RC, Borisuth NS, Tripathi Bj. Detection,quantification, and significance of basic fibroblast growthfactor in the aqueous humor of man, cat, dog and pig. ExpEye Res,1992;54(3):447-454.Tripathi RC, Borisuth NS, Tripathi Bj. Detection,quantification, and significance of basic fibroblast growthfactor in the aqueous humor of man, cat, dog and pig. ExpEye Res,1992;54(3):447-454.
8、Johnstone EW,Wong HC, Coster DJ, et al. Factorsaffecting bovine corneal endothelial cell density in vitro.British Joural of Ophthalmology, 1996; 80(3):256-262.Johnstone EW,Wong HC, Coster DJ, et al. Factorsaffecting bovine corneal endothelial cell density in vitro.British Joural of Ophthalmology, 1996; 80(3):256-262.
9、Woost PG,Jumblatt MM, Eifeman RA, et al. Growthfactors and corneal endothelial cells: 1. Stimulation ofbovine comeal endothelial cell DNA synthesis by definedgrowth factors.Corea,1992;11(1):1-10.Woost PG,Jumblatt MM, Eifeman RA, et al. Growthfactors and corneal endothelial cells: 1. Stimulation ofbovine comeal endothelial cell DNA synthesis by definedgrowth factors.Corea,1992;11(1):1-10.
10、Schultz G,CipollaL,Whitehouse A, et al. Growthfactors and corneal endothelial cells: . Stimulalion ofadult human comeal endothelial cell mitoeis in vitro bydefined mitogenic agents.Comea,1992;11(1):20-27Schultz G,CipollaL,Whitehouse A, et al. Growthfactors and corneal endothelial cells: . Stimulalion ofadult human comeal endothelial cell mitoeis in vitro bydefined mitogenic agents.Comea,1992;11(1):20-27
11、Hoppenreijs VP, Pels E, Vrensen GF, et al. Effects ofhuman epidermal growth factor on endothelial woundhealing of human comeas.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,1992;33(6):1946-1957.Hoppenreijs VP, Pels E, Vrensen GF, et al. Effects ofhuman epidermal growth factor on endothelial woundhealing of human comeas.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,1992;33(6):1946-1957.
12、Joyce NC,ZhuCC. Human comeal endothelial cellproliferation: potential for use in regenerative medicine.Comea,2004,23(8 Suppl):S8-S19.Joyce NC,ZhuCC. Human comeal endothelial cellproliferation: potential for use in regenerative medicine.Comea,2004,23(8 Suppl):S8-S19.
13、Lambiase A, Bonini S, Manni L. intraocular productionand release of nerve growth factor after iridectomy, InvestOphthalmol Vis Sci,2002,43(7):2334-2340.Lambiase A, Bonini S, Manni L. intraocular productionand release of nerve growth factor after iridectomy, InvestOphthalmol Vis Sci,2002,43(7):2334-2340.