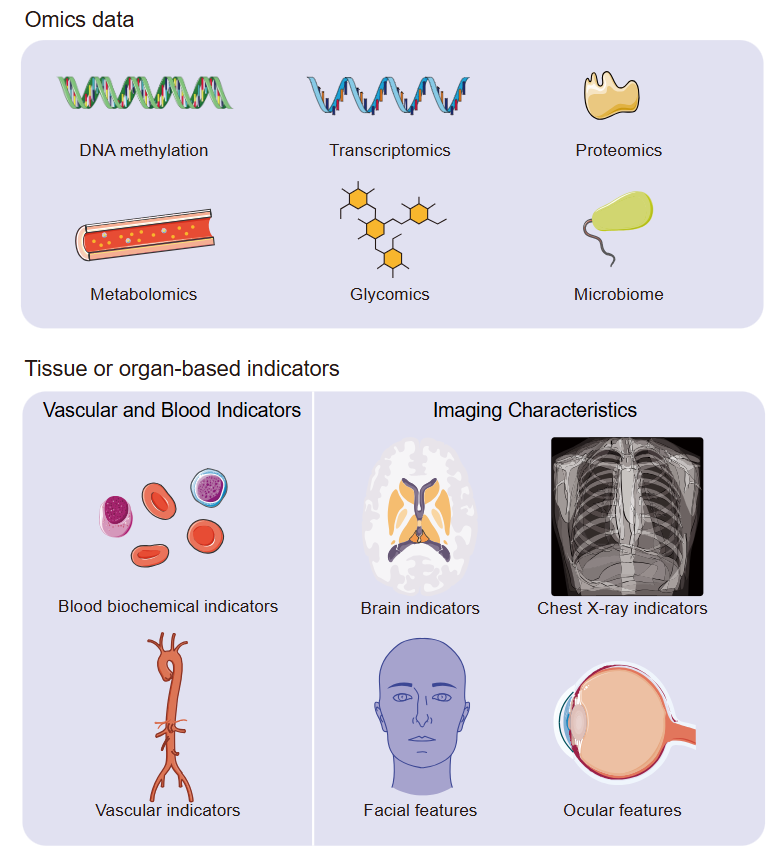
1、Hamczyk MR, Nevado RM, Barettino A, et al. Biological
versus chronological aging: JACC focus seminar. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 2020, 75(8): 919-930. DOI: 10.1016/
j.jacc.2019.11.062.Hamczyk MR, Nevado RM, Barettino A, et al. Biological
versus chronological aging: JACC focus seminar. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 2020, 75(8): 919-930. DOI: 10.1016/
j.jacc.2019.11.062.
2、Levine%20ME.%20Modeling%20the%20rate%20of%20senescence%3A%20can%0Aestimated%20biological%20age%20predict%20mortality%20more%20accurately%20%0Athan%20chronological%20age%3F%20J%20Gerontol%20A%20Biol%20Sci%20Med%20Sci.%0A2013%2C%2068(6)%3A%20667-674.%20DOI%3A%2010.1093%2Fgerona%2Fgls233.Levine%20ME.%20Modeling%20the%20rate%20of%20senescence%3A%20can%0Aestimated%20biological%20age%20predict%20mortality%20more%20accurately%20%0Athan%20chronological%20age%3F%20J%20Gerontol%20A%20Biol%20Sci%20Med%20Sci.%0A2013%2C%2068(6)%3A%20667-674.%20DOI%3A%2010.1093%2Fgerona%2Fgls233.
3、Kang YG, Suh E, Lee JW, et al. Biological age as a health
index for mortality and major age-related disease incidence
in Koreans: national Health Insurance Service - Health
screening 11-year follow-up study. Clin Interv Aging.
2018, 13: 429-436. DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S157014.Kang YG, Suh E, Lee JW, et al. Biological age as a health
index for mortality and major age-related disease incidence
in Koreans: national Health Insurance Service - Health
screening 11-year follow-up study. Clin Interv Aging.
2018, 13: 429-436. DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S157014.
4、Rutledge J, Oh H, Wyss-Coray T. Measuring biological
age using omics data. Nat Rev Genet. 2022, 23(12): 715-
727. DOI: 10.1038/s41576-022-00511-7.Rutledge J, Oh H, Wyss-Coray T. Measuring biological
age using omics data. Nat Rev Genet. 2022, 23(12): 715-
727. DOI: 10.1038/s41576-022-00511-7.
5、Hashmi S. ‘Coming of Age’ of artificial intelligence:
evolution of survivorship care through information
technology. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51(1): 41-42.
DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2015.271.Hashmi S. ‘Coming of Age’ of artificial intelligence:
evolution of survivorship care through information
technology. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51(1): 41-42.
DOI: 10.1038/bmt.2015.271.
6、Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the
lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B: Methodol. 1996, 58: 267-288.
DOI: 10.1111/J.2517-6161.1996.TB02080.X.Tibshirani R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the
lasso. J R Stat Soc Ser B: Methodol. 1996, 58: 267-288.
DOI: 10.1111/J.2517-6161.1996.TB02080.X.
7、Hilt D, Seegrist DW. Ridge, a computer program for
calculating ridge regression estimates.1977.Hilt D, Seegrist DW. Ridge, a computer program for
calculating ridge regression estimates.1977.
8、Zou H, Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection
via the elastic net. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society
Series B: Statistical Methodology. 2005, 67(2): 301-320.
DOI: 10.1111/biom.12868.Zou H, Hastie T. Regularization and variable selection
via the elastic net. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society
Series B: Statistical Methodology. 2005, 67(2): 301-320.
DOI: 10.1111/biom.12868.
9、Platt J. Probabilistic outputs for support vector machines
and comparisons to regularized likelihood methods.
Advances in large margin classifiers. 1999, 10(3): 61-74.Platt J. Probabilistic outputs for support vector machines
and comparisons to regularized likelihood methods.
Advances in large margin classifiers. 1999, 10(3): 61-74.
10、Breiman L. Random forests. Machine learning. 2001,
45(1): 5-32.Breiman L. Random forests. Machine learning. 2001,
45(1): 5-32.
11、Hinton G E. Connectionist learning procedures//Machine
learning. Morgan Kaufmann, 1990: 555-610.Hinton G E. Connectionist learning procedures//Machine
learning. Morgan Kaufmann, 1990: 555-610.
12、Alzubaidi L, Zhang J, Humaidi AJ, et al. Review of
deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges,
applications, future directions. J Big Data. 2021, 8(1): 53.
DOI: 10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8.Alzubaidi L, Zhang J, Humaidi AJ, et al. Review of
deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges,
applications, future directions. J Big Data. 2021, 8(1): 53.
DOI: 10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8.
13、Hannum G, Guinney J, Zhao L, et al. Genome-wide
methylation profiles reveal quantitative views of human
aging rates. Mol Cell. 2013, 49(2): 359-367. DOI:
10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.016.Hannum G, Guinney J, Zhao L, et al. Genome-wide
methylation profiles reveal quantitative views of human
aging rates. Mol Cell. 2013, 49(2): 359-367. DOI:
10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.016.
14、Horvath S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell
types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14(10): R115. DOI: 10.1186/
gb-2013-14-10-r115.Horvath S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell
types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14(10): R115. DOI: 10.1186/
gb-2013-14-10-r115.
15、Levine ME, Lu AT, Quach A, et al. An epigenetic
biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan. Aging.
2018, 10(4): 573-591. DOI: 10.18632/aging.101414.Levine ME, Lu AT, Quach A, et al. An epigenetic
biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan. Aging.
2018, 10(4): 573-591. DOI: 10.18632/aging.101414.
16、Lu AT, Quach A, Wilson JG, et al. DNA methylation
GrimAge strongly predicts lifespan and healthspan. Aging.
2019, 11(2): 303-327. DOI: 10.18632/aging.101684.Lu AT, Quach A, Wilson JG, et al. DNA methylation
GrimAge strongly predicts lifespan and healthspan. Aging.
2019, 11(2): 303-327. DOI: 10.18632/aging.101684.
17、Zhang Y, Wilson R, Heiss J, et al. DNA methylation
signatures in peripheral blood strongly predict all-cause
mortality. Nat Commun. 2017, 8: 14617. DOI: 10.1038/
ncomms14617.Zhang Y, Wilson R, Heiss J, et al. DNA methylation
signatures in peripheral blood strongly predict all-cause
mortality. Nat Commun. 2017, 8: 14617. DOI: 10.1038/
ncomms14617.
18、López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, et al., The
hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013. 153(6): 1194-1217. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039.López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, et al., The
hallmarks of aging. Cell. 2013. 153(6): 1194-1217. DOI:
10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039.
19、Bocklandt S, Lin W, Sehl ME, et al. Epigenetic predictor
of age. PLoS One. 2011, 6(6): e14821. DOI: 10.1371/
journal.pone.0014821.Bocklandt S, Lin W, Sehl ME, et al. Epigenetic predictor
of age. PLoS One. 2011, 6(6): e14821. DOI: 10.1371/
journal.pone.0014821.
20、Verschoor CP, Lin DTS, Kobor MS, et al. Epigenetic age
is associated with baseline and 3-year change in frailty in
the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Clin Epigenet.
2021, 13(1): 163. DOI: 10.1186/s13148-021-01150-1.Verschoor CP, Lin DTS, Kobor MS, et al. Epigenetic age
is associated with baseline and 3-year change in frailty in
the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Clin Epigenet.
2021, 13(1): 163. DOI: 10.1186/s13148-021-01150-1.
21、Maddock J, Castillo-Fernandez J, Wong A, et al. DNA
methylation age and physical and cognitive ageing. J
Gerontol Ser A. 2020:75(3):504-511.. DOI: 10.1093/
gerona/glz246.Maddock J, Castillo-Fernandez J, Wong A, et al. DNA
methylation age and physical and cognitive ageing. J
Gerontol Ser A. 2020:75(3):504-511.. DOI: 10.1093/
gerona/glz246.
22、McCrory C, Fiorito G, Hernandez B, et al. GrimAge
outperforms other epigenetic clocks in the prediction of
age-related clinical phenotypes and all-cause mortality.
J Gerontol Ser A. 2021, 76(5): 741-749. DOI: 10.1093/
gerona/glaa286.McCrory C, Fiorito G, Hernandez B, et al. GrimAge
outperforms other epigenetic clocks in the prediction of
age-related clinical phenotypes and all-cause mortality.
J Gerontol Ser A. 2021, 76(5): 741-749. DOI: 10.1093/
gerona/glaa286.
23、Hillary RF, Stevenson AJ, Cox SR, et al. An epigenetic
predictor of death captures multi-modal measures of
brain health. Mol Psychiatry. 2021, 26: 3806-3816. DOI:
10.1038/s41380-019-0616-9.Hillary RF, Stevenson AJ, Cox SR, et al. An epigenetic
predictor of death captures multi-modal measures of
brain health. Mol Psychiatry. 2021, 26: 3806-3816. DOI:
10.1038/s41380-019-0616-9.
24、Peters MJ, Joehanes R, Pilling LC, et al. The
transcriptional landscape of age in human peripheral blood.
Nat Commun. 2015, 6: 8570. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9570.Peters MJ, Joehanes R, Pilling LC, et al. The
transcriptional landscape of age in human peripheral blood.
Nat Commun. 2015, 6: 8570. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9570.
25、Fleischer JG, Schulte R, Tsai HH, et al. Predicting age
from the transcriptome of human dermal fibroblasts.
Genome Biol. 2018, 19(1): 221. DOI: 10.1186/s13059-
018-1599-6.Fleischer JG, Schulte R, Tsai HH, et al. Predicting age
from the transcriptome of human dermal fibroblasts.
Genome Biol. 2018, 19(1): 221. DOI: 10.1186/s13059-
018-1599-6.
26、Holzscheck%20N%2C%20Falckenhayn%20C%2C%20S%C3%B6hle%20J%2C%20et%20al.%20Modeling%0Atranscriptomic%20age%20using%20knowledge-primed%20artificial%20%0Aneural%20networks.%20NPJ%20Aging%20Mech%20Dis.%202021%2C7(1)%3A15.%20DOI%3A%0A10.1038%2Fs41514-021-00068-5.Holzscheck%20N%2C%20Falckenhayn%20C%2C%20S%C3%B6hle%20J%2C%20et%20al.%20Modeling%0Atranscriptomic%20age%20using%20knowledge-primed%20artificial%20%0Aneural%20networks.%20NPJ%20Aging%20Mech%20Dis.%202021%2C7(1)%3A15.%20DOI%3A%0A10.1038%2Fs41514-021-00068-5.
27、Ignjatovic V, Lai C, Summerhayes R, et al. Age-related
differences in plasma proteins: how plasma proteins
change from neonates to adults. PLoS One. 2011, 6(2):
e17213. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017213.Ignjatovic V, Lai C, Summerhayes R, et al. Age-related
differences in plasma proteins: how plasma proteins
change from neonates to adults. PLoS One. 2011, 6(2):
e17213. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017213.
28、Baird GS, Nelson SK, Keeney TR, et al. Age-dependent
changes in the cerebrospinal fluid proteome by slow off�rate modified aptamer array. Am J Pathol. 2012, 180(2):
446-456. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.024.Baird GS, Nelson SK, Keeney TR, et al. Age-dependent
changes in the cerebrospinal fluid proteome by slow off�rate modified aptamer array. Am J Pathol. 2012, 180(2):
446-456. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.024.
29、Menni, C., et al., Circulating proteomic signatures of
chronological age. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015,
70(7): 809-816. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glu121.Menni, C., et al., Circulating proteomic signatures of
chronological age. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015,
70(7): 809-816. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glu121.
30、Tanaka T, Biancotto A, Moaddel R, et al. Plasma
proteomic signature of age in healthy humans. Aging Cell.
2018, 17(5): e12799. DOI: 10.1111/acel.12799.Tanaka T, Biancotto A, Moaddel R, et al. Plasma
proteomic signature of age in healthy humans. Aging Cell.
2018, 17(5): e12799. DOI: 10.1111/acel.12799.
31、Lehallier B, Gate D, Schaum N, et al. Undulating changes
in human plasma proteome profiles across the lifespan.
Nat Med. 2019, 25(12): 1843-1850. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-
019-0673-2.Lehallier B, Gate D, Schaum N, et al. Undulating changes
in human plasma proteome profiles across the lifespan.
Nat Med. 2019, 25(12): 1843-1850. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-
019-0673-2.
32、Wolf J, Rasmussen DK, Sun YJ, et al. Liquid-biopsy
proteomics combined with AI identifies cellular drivers of
eye aging and disease in vivo. Cell. 2023, 186(22): 4868-
4884.e12. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.012.Wolf J, Rasmussen DK, Sun YJ, et al. Liquid-biopsy
proteomics combined with AI identifies cellular drivers of
eye aging and disease in vivo. Cell. 2023, 186(22): 4868-
4884.e12. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.09.012.
33、Deelen J, Kettunen J, Fischer K, et al. A metabolic profile
of all-cause mortality risk identified in an observational
study of 44, 168 individuals. Nat Commun. 2019, 10:
3346. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11311-9.Deelen J, Kettunen J, Fischer K, et al. A metabolic profile
of all-cause mortality risk identified in an observational
study of 44, 168 individuals. Nat Commun. 2019, 10:
3346. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11311-9.
34、van den Akker EB, Trompet S, Barkey Wolf JJH, et
al. Metabolic age based on the BBMRI-NL 1H-NMR
metabolomics repository as biomarker of age-related
disease. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2020, 13(5): 541-547. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.119.002610.van den Akker EB, Trompet S, Barkey Wolf JJH, et
al. Metabolic age based on the BBMRI-NL 1H-NMR
metabolomics repository as biomarker of age-related
disease. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2020, 13(5): 541-547. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.119.002610.
35、Robinson O, Chadeau Hyam M, Karaman I, et al.
Determinants of accelerated metabolomic and epigenetic
aging in a UK cohort. Aging Cell. 2020, 19(6): e13149.
DOI: 10.1111/acel.13149.Robinson O, Chadeau Hyam M, Karaman I, et al.
Determinants of accelerated metabolomic and epigenetic
aging in a UK cohort. Aging Cell. 2020, 19(6): e13149.
DOI: 10.1111/acel.13149.
36、Hertel J, Friedrich N, Wittfeld K, et al. Measuring
biological age via metabonomics: the metabolic age score.
J Proteome Res. 2016, 15(2): 400-410. DOI: 10.1021/acs.
jproteome.5b00561.Hertel J, Friedrich N, Wittfeld K, et al. Measuring
biological age via metabonomics: the metabolic age score.
J Proteome Res. 2016, 15(2): 400-410. DOI: 10.1021/acs.
jproteome.5b00561.
37、Le%20Couteur%20DG%2C%20Simpson%20SJ%2C%20de%20Cabo%20R.%20Are%20glycans%20the%20%0Aholy%20grail%20for%20biomarkers%20of%20aging%3F%20(comment%20on%3A%20glycans%0Aare%20a%20novel%20biomarker%20of%20chronological%20and%20biological%20age%0Aby%20kristic%20et%20Al.).%20J%20Gerontol%20Ser%20A%20Biol%20Sci%20Med%20Sci.%202014%2C%0A69(7)%3A%20777-778.%20DOI%3A%2010.1093%2Fgerona%2Fglt202.Le%20Couteur%20DG%2C%20Simpson%20SJ%2C%20de%20Cabo%20R.%20Are%20glycans%20the%20%0Aholy%20grail%20for%20biomarkers%20of%20aging%3F%20(comment%20on%3A%20glycans%0Aare%20a%20novel%20biomarker%20of%20chronological%20and%20biological%20age%0Aby%20kristic%20et%20Al.).%20J%20Gerontol%20Ser%20A%20Biol%20Sci%20Med%20Sci.%202014%2C%0A69(7)%3A%20777-778.%20DOI%3A%2010.1093%2Fgerona%2Fglt202.
38、Galkin F, Mamoshina P, Aliper A, et al. Human gut
microbiome aging clock based on taxonomic profiling
and deep learning. iScience. 2020, 23(6): 101199. DOI:
10.1016/j.isci.2020.101199.Galkin F, Mamoshina P, Aliper A, et al. Human gut
microbiome aging clock based on taxonomic profiling
and deep learning. iScience. 2020, 23(6): 101199. DOI:
10.1016/j.isci.2020.101199.
39、Putin E, Mamoshina P, Aliper A, et al. Deep biomarkers
of human aging: application of deep neural networks to
biomarker development. Aging. 2016, 8(5): 1021-1033.
DOI: 10.18632/aging.100968.Putin E, Mamoshina P, Aliper A, et al. Deep biomarkers
of human aging: application of deep neural networks to
biomarker development. Aging. 2016, 8(5): 1021-1033.
DOI: 10.18632/aging.100968.
40、Mamoshina P, Kochetov K, Putin E, et al. Population
specific biomarkers of human aging: a big data study using
South Korean, Canadian, and eastern European patient
populations. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018,
73(11): 1482-1490. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/gly005.Mamoshina P, Kochetov K, Putin E, et al. Population
specific biomarkers of human aging: a big data study using
South Korean, Canadian, and eastern European patient
populations. J Gerontol Ser A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2018,
73(11): 1482-1490. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/gly005.
41、Mamoshina P, Kochetov K, Cortese F, et al. Blood
biochemistry analysis to detect smoking status and
quantify accelerated aging in smokers. Sci Rep. 2019,
9(1): 142. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-35704-w.Mamoshina P, Kochetov K, Cortese F, et al. Blood
biochemistry analysis to detect smoking status and
quantify accelerated aging in smokers. Sci Rep. 2019,
9(1): 142. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-35704-w.
42、Liu Z, Kuo PL, Horvath S, et al. A new aging measure
captures morbidity and mortality risk across diverse
subpopulations from NHANES IV: a cohort study. PLoS
Med. 2018, 15(12): e1002718. DOI: 10.1371/journal.
pmed.1002718.Liu Z, Kuo PL, Horvath S, et al. A new aging measure
captures morbidity and mortality risk across diverse
subpopulations from NHANES IV: a cohort study. PLoS
Med. 2018, 15(12): e1002718. DOI: 10.1371/journal.
pmed.1002718.
43、Abbott A. Dementia: a problem for our age. Nature, 2011,
475(7355): S2-S4. DOI: 10.1038/475S2a.Abbott A. Dementia: a problem for our age. Nature, 2011,
475(7355): S2-S4. DOI: 10.1038/475S2a.
44、Cole JH, Ritchie SJ, Bastin ME, et al. Brain age predicts
mortality. Mol Psychiatry. 2018, 23(5): 1385-1392. DOI:
10.1038/mp.2017.62.Cole JH, Ritchie SJ, Bastin ME, et al. Brain age predicts
mortality. Mol Psychiatry. 2018, 23(5): 1385-1392. DOI:
10.1038/mp.2017.62.
45、Elliott ML, Belsky DW, Knodt AR, et al. Brain-age in
midlife is associated with accelerated biological aging
and cognitive decline in a longitudinal birth cohort.
Mol Psychiatry. 2021, 26(8): 3829-3838. DOI: 10.1038/
s41380-019-0626-7.Elliott ML, Belsky DW, Knodt AR, et al. Brain-age in
midlife is associated with accelerated biological aging
and cognitive decline in a longitudinal birth cohort.
Mol Psychiatry. 2021, 26(8): 3829-3838. DOI: 10.1038/
s41380-019-0626-7.
46、Bulpitt CJ, Rajkumar C, Cameron JD. Cameron, Vascular
compliance as a measure of biological age. J Am Geriatr
Soc. 1999,47(6):657-63. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1999.
tb01586.x.Bulpitt CJ, Rajkumar C, Cameron JD. Cameron, Vascular
compliance as a measure of biological age. J Am Geriatr
Soc. 1999,47(6):657-63. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1999.
tb01586.x.
47、McClelland RL, Nasir K, Budoff M, et al. Arterial age as a
function of coronary artery calcium (from the Multi-Ethnic
Study of Atherosclerosis[MESA]). Am J Cardiol. 2009,
103(1): 59-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.08.031.McClelland RL, Nasir K, Budoff M, et al. Arterial age as a
function of coronary artery calcium (from the Multi-Ethnic
Study of Atherosclerosis[MESA]). Am J Cardiol. 2009,
103(1): 59-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.08.031.
48、Nilsson%20Wadstr%C3%B6m%20B%2C%20Fatehali%20AA%20H%2C%20Engstr%C3%B6m%20G%2C%20et%0Aal.%20A%20vascular%20aging%20index%20as%20independent%20predictor%20of%0Acardiovascular%20events%20and%20total%20mortality%20in%20an%20elderly%0Aurban%20population.%20Angiology.%202019%2C%2070(10)%3A%20929-937.%20DOI%3A%0A10.1177%2F0003319719857270.Nilsson%20Wadstr%C3%B6m%20B%2C%20Fatehali%20AA%20H%2C%20Engstr%C3%B6m%20G%2C%20et%0Aal.%20A%20vascular%20aging%20index%20as%20independent%20predictor%20of%0Acardiovascular%20events%20and%20total%20mortality%20in%20an%20elderly%0Aurban%20population.%20Angiology.%202019%2C%2070(10)%3A%20929-937.%20DOI%3A%0A10.1177%2F0003319719857270.
49、G a l e C R , C o o p e r C , S a y e r A A . F r a m i n g h a m
cardiovascular disease risk scores and incident frailty: the
English longitudinal study of ageing. AGE. 2014, 36(4):
9692. DOI: 10.1007/s11357-014-9692-6.G a l e C R , C o o p e r C , S a y e r A A . F r a m i n g h a m
cardiovascular disease risk scores and incident frailty: the
English longitudinal study of ageing. AGE. 2014, 36(4):
9692. DOI: 10.1007/s11357-014-9692-6.
50、Raghu VK, Weiss J, Hoffmann U, et al. Deep learning to
estimate biological age from chest radiographs. JACC
Cardiovasc Imag. 2021, 14(11): 2226-2236. DOI: 10.1016/
j.jcmg.2021.01.008.Raghu VK, Weiss J, Hoffmann U, et al. Deep learning to
estimate biological age from chest radiographs. JACC
Cardiovasc Imag. 2021, 14(11): 2226-2236. DOI: 10.1016/
j.jcmg.2021.01.008.
51、Christensen K, Thinggaard M, McGue M, et al. Perceived
age as clinically useful biomarker of ageing: cohort study.
BMJ. 2009, 339: b5262. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.b5262.Christensen K, Thinggaard M, McGue M, et al. Perceived
age as clinically useful biomarker of ageing: cohort study.
BMJ. 2009, 339: b5262. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.b5262.
52、Xia X, Chen X, Wu G, et al. Three-dimensional facial�image analysis to predict heterogeneity of the human ageing rate and the impact of lifestyle. Nat Metab. 2020,
2(9): 946-957. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-020-00270-x.Xia X, Chen X, Wu G, et al. Three-dimensional facial�image analysis to predict heterogeneity of the human ageing rate and the impact of lifestyle. Nat Metab. 2020,
2(9): 946-957. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-020-00270-x.
53、Yu Z, Zhou Y, Mao K, et al. Thermal facial image analyses
reveal quantitative hallmarks of aging and metabolic
diseases. Cell Metab. 2024, 36(7): 1482-1493.e7. DOI:
10.1016/j.cmet.2024.05.012.Yu Z, Zhou Y, Mao K, et al. Thermal facial image analyses
reveal quantitative hallmarks of aging and metabolic
diseases. Cell Metab. 2024, 36(7): 1482-1493.e7. DOI:
10.1016/j.cmet.2024.05.012.
54、Zhu Z, Shi D, Guankai P, et al. Retinal age gap as a
predictive biomarker for mortality risk. Br J Ophthalmol.
2023, 107(4): 547-554. DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol- 2021-
319807.Zhu Z, Shi D, Guankai P, et al. Retinal age gap as a
predictive biomarker for mortality risk. Br J Ophthalmol.
2023, 107(4): 547-554. DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol- 2021-
319807.
55、Hu W, Wang W, Wang Y, et al. Retinal age gap as a
predictive biomarker of future risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Age Ageing. 2022, 51(3): afac062. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/
afac062.Hu W, Wang W, Wang Y, et al. Retinal age gap as a
predictive biomarker of future risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Age Ageing. 2022, 51(3): afac062. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/
afac062.
56、Nusinovici S, Rim TH, Yu M, et al. Retinal photograph�based deep learning predicts biological age, and stratifies
morbidity and mortality risk. Age Ageing. 2022, 51(4):
afac065. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afac065.Nusinovici S, Rim TH, Yu M, et al. Retinal photograph�based deep learning predicts biological age, and stratifies
morbidity and mortality risk. Age Ageing. 2022, 51(4):
afac065. DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afac065.
57、Liu C, Wang W, Li Z, et al. Biological age estimated from
retinal imaging: a novel biomarker of aging[M]//Lecture
Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International
Publishing. 2019: 138-146. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-
32239-7_16.Liu C, Wang W, Li Z, et al. Biological age estimated from
retinal imaging: a novel biomarker of aging[M]//Lecture
Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International
Publishing. 2019: 138-146. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-
32239-7_16.
58、Li R, Chen W, Li M, et al. LensAge index as a deep
learning-based biological age for self-monitoring the risks
of age-related diseases and mortality. Nat Commun. 2023,
14(1): 7126. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42934-8.Li R, Chen W, Li M, et al. LensAge index as a deep
learning-based biological age for self-monitoring the risks
of age-related diseases and mortality. Nat Commun. 2023,
14(1): 7126. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42934-8.
59、Li Q, Wang S, Milot E, et al. Homeostatic dysregulation
proceeds in parallel in multiple physiological systems.
Aging Cell. 2015, 14(6): 1103-1112. DOI: 10.1111/acel.
12402.Li Q, Wang S, Milot E, et al. Homeostatic dysregulation
proceeds in parallel in multiple physiological systems.
Aging Cell. 2015, 14(6): 1103-1112. DOI: 10.1111/acel.
12402.
60、Belsky%20DW%2C%20Moffitt%20TE%2C%20Cohen%20AA%2C%20et%20al.%20Eleven%20telomere%2C%0Aepigenetic%20clock%2C%20and%20biomarker-composite%20quantifications%0Aof%20biological%20aging%3A%20do%20they%20measure%20the%20same%20thing%3F%20Am%20J%0AEpidemiol.%202018%20Jun%201%3B%20187(6)%3A1220-1230.%20DOI%3A%2010.1093%2F%0Aaje%2Fkwx346.Belsky%20DW%2C%20Moffitt%20TE%2C%20Cohen%20AA%2C%20et%20al.%20Eleven%20telomere%2C%0Aepigenetic%20clock%2C%20and%20biomarker-composite%20quantifications%0Aof%20biological%20aging%3A%20do%20they%20measure%20the%20same%20thing%3F%20Am%20J%0AEpidemiol.%202018%20Jun%201%3B%20187(6)%3A1220-1230.%20DOI%3A%2010.1093%2F%0Aaje%2Fkwx346.